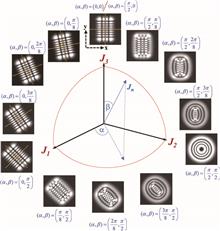
The study of structured laser beams has been one of the most active fields of research for decades, particularly in exploring laser beams with orbital angular momentum. The direct generation of structured beams from laser resonators is deeply associated with the formation of transverse modes. The wave representations of transverse modes of spherical cavities are usually categorized into Hermite–Gaussian (HG) and Laguerre–Gaussian (LG) modes for a long time. Enormous experimental results have revealed that the generalized representation for the transverse modes is the Hermite–LG (HLG) modes. We make a detailed overview for the theoretical description of the HLG modes from the representation of the spectral unitary group of order 2 in the Jordan–Schwinger map. Furthermore, we overview how to derive the integral formula for the elliptical modes based on the Gaussian wave-packet state and the inverse Fourier transform. The relationship between the HLG modes and elliptical modes is linked by the quantum Fourier transform. The most striking result is that the HLG modes can be exactly derived as the superposition of the elliptical modes without involving Hermite and Laguerre polynomials. Finally, we discuss the application of the HLG modes in characterizing the propagation evolution of the vortex structures of HG beams transformed by an astigmatic mode converter. This overview certainly provides not only a novel formula for transverse modes, but also a pedagogical insight into quantum physics.
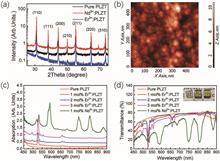
The broadband photochromic effect on undoped and rare-earth-doped lead lanthanum zirconate titanate (PLZT) ceramics was studied under the illumination of ultraviolet light at 360 nm. The photocarriers’ trapping and detrapping processes of thermal disconnected traps played the vital role in both darkening and bleaching processes. The interaction between photocarrier traps and rare-earth ion energy levels was demonstrated, which influenced the photochromatic darkening performance greatly. The transformation of photoluminescence spectra in Er3+-doped PLZT ceramics also improved the physical picture of the trap’s distribution of the materials. This work could be used to modulate the photoluminescence and lasing behavior.
A novel four light ray path test method for measuring residual reflectance has been presented. Residual reflectance spatial distribution at a cladding interface was measured using the technique. Residual reflectance could be on the order of 10?5 by matching the refractive index of Nd:glass, polymer, and cladding glass and eliminating defects in the adhesive layer. Residual reflection spatial distribution appears to be similar to Newton rings due to the edge surface flatness. The relationship between the residual reflectance and the edge surface flatness was discussed, and the results revealed that the edge surface flatness is very important during the cladding process.
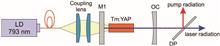
Detailed power and spectral analysis of a diode-pumped c-cut Pbnm 3 at.% Tm-doped yttrium aluminum perovskite (Tm:YAP) laser in a continuous wave (CW) operation is presented. The laser was experimentally examined in terms of the dependence on the transmittance and radius of curvature of the output coupling mirrors. At room temperature, for an output coupling transmission of 10.8%, the maximum output power of 6.35 W was obtained under a total absorbed pump power of 13.67 W with an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 46.5%. The highest slope efficiency of 60.4% was indicated. A detailed spectral analysis was presented. For its dependence on output coupler transmission, the Tm:YAP laser generates wavelengths at approximately 1940 nm or 1990 nm.
High-repetition-rate (HRR) pulsed fiber lasers have attracted much attention in various fields. To effectively achieve HRR pulses in fiber lasers, dissipative four-wave-mixing mode-locking is a promising method. In this work, we demonstrated an HRR pulsed fiber laser based on a virtually imaged phased array (VIPA), serving as a comb filter. Due to the high spectral resolution and low polarization sensitivity features of VIPA, the 30 GHz pulse with high quality and high stability could be obtained. In the experiments, both the single-waveband and dual-waveband HRR pulses were achieved. Such an HRR pulsed fiber laser could have potential applications in related fields, such as optical communications.
Pulses as short as 8.1 fs were generated from a blue laser-diode-pumped Kerr-lens mode-locked Ti:sapphire oscillator, with an average power of 27 mW and a repetition rate of 120.6 MHz. The full width at half-maximum exceeds 146 nm, benefitting from the dispersion management by a combination of a low-dispersion fused silica prism pair and a series of double-chirped mirrors. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time to generate sub-10-fs pulses from a laser diode directly pumped Ti:sapphire oscillator.
We report 25 Gb/s high-speed directly modulated ground-state operation of 1.3 μm InAs/GaAs quantum dot (QD) lasers grown by molecular beam epitaxy. The active region of the lasers consists of eight layers of p-doped InAs QDs with high uniformity and density. Ridge-waveguide lasers with a 3-μm-wide and 300-μm-long cavity show a low threshold current of 14.4 mA at 20°C and high temperature stability with a high characteristic temperature of 1208 K between 20°C and 70°C. Dynamic response measurements demonstrate that the laser has a 3 dB bandwidth of 7.7 GHz at 20°C and clearly opened eye diagrams even at high temperatures up to 75°C under a 25 Gb/s direct modulation rate.
The point clouds scanned by a 3D laser scanner may be affine transformed when the size and posture of the objects being scanned are different. This type of problem is common, but few algorithms can solve it. Therefore, this Letter proposes a parallel registration algorithm. The algorithm eliminates the effects of the affine matrix in the point cloud, based on a simple whitening operation. Moreover, it also has strong anti-noise performance. The algorithm proposed in this Letter is not only simple in structure, but also shows excellent effects in practical applications and simulations.
A 21.2 kW, 1.94 times the diffraction-limit quasi-continuous-wave laser is presented in this Letter based on a multi-stage, power-scalable Yb:YAG master-oscillator-power-amplifier (MOPA) system under adaptive optics (AO) control. The output laser of the MOPA system is a rectangular beam with a length-width ratio of 2:1, a 200 μs pulse duration, and a 1000 Hz repetition rate. With the AO control system, the beam quality of the laser is improved from 4.20 to 1.94 times the diffraction limit. To our knowledge, this is the best quality laser in the 20 kW class except for combined lasers.
We experimentally demonstrated that the distributed feedback (DFB) lasers with the active distributed reflector achieved a 25.8 Gb/s operation over a wide temperature range of ?40 to 85°C. The DFB lasers can achieve additional feedback from an active distributed reflector with accurately controlled phase, and single-mode yields are not related to the position of cleave. The threshold currents of the fabricated laser are 6 mA and 20 mA at ?40°C and 85°C, respectively. The side mode suppression ratio of the fabricated laser is above 50 dB at all temperatures. Transmissions of 25.8 Gb/s after 10 km single-mode fibers with clear eye openings and less than 0.8 dB power penalty over a wide temperature range have been demonstrated as well.
Laser-induced discharge plasmas (LDPs) have the potential to be inspection and metrology sources in extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography. An LDP EUV source was developed to avoid tin electrode erosion in which a tin pool was used as a cathode. A CO2 pulse laser was focused on the liquid tin target surface, and then a breakdown occurred in a very short time. The voltage-current characteristics of the discharge oscillated, lasting for several microseconds, and an RLC fitting model was used to obtain the inductance and resistance. An intensified charge-coupled device (ICCD) camera was used to investigate the dynamics of LDP, which can explain the formation of a discharge channel. The EUV spectra of laser-induced liquid tin discharge plasma were detected by a grazing incident ultraviolet spectrometer, compared with a laser-produced tin droplet plasma EUV spectrum. To explain the EUV spectrum difference of laser-induced liquid tin discharge plasma and laser-produced tin droplet plasma, the collision radiation (CR) model combined with COWAN code was used to fit the experimental EUV spectrum, which can estimate the electron temperature and density of the plasma.
The ultimate capacity of a cladding-pumped 10/130 Tm:fiber is experimentally investigated with a 793 nm laser diode bidirectionally pumped amplifier. The laser system works stably at the output powers of 52 W, 65 W, and 87 W. Eventually, the damage of the amplifier occurs when the output power reaches about 103.5 W with a total incident pump power of 176.8 W. Considering the incident seed power of 12.3 W, the amplifier conversion efficiency is estimated to be about 51.6% before it is damaged. With valuable exploration, we achieve the first air-cooling 60 W Tm:fiber laser at 1945.845 nm with a spectral linewidth of 0.4 nm. The laser power stability reaches 1.24% during a continuous test time of >65 h. The beam quality is measured as Mx2=1.16 and My2=1.14.
The unamplified spontaneous emission (SE) is one of the important physical processes of the light–matter interaction in a diode laser in terms of Einstein’s theory. The recent research on a kind of new indium-rich cluster (IRC) laser structure did not reveal SE characteristics of the IRC structure, as its unusual quantum confined structure made it difficult to acquire correctly the SE spectra through theoretical simulation or previous experimental techniques. Thus, in this Letter, we firstly established a convenient and effective experimental approach to acquire SE spectra of the IRC structure by the measurement of amplified SEs from dual facets of a single edge-emitting chip with little sample processing. With the proposed method, the special SE spectra due to the IRC effect were observed. Then, the SE formation mechanism and characteristics in the IRC structure were analyzed by comparing the experimental data with theoretical SE spectra using a standard InGaAs/GaAs quantum well with similar material composition. This research provides a useful tool to investigate the SE characteristics of any non-standard diode laser structure and is very meaningful to develop a new type of IRC lasers.
In this work, SF6 as a Raman-active medium is investigated to generate a multispectral Raman laser by the combination of cascade stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) and four wave mixing. The Raman frequency comb from the 10th-order anti-Stokes to the 9th-order Stokes was generated, and its spectral range covered 377–846 nm. The photon conversion efficiency of 16.4% for the first Stokes was achieved, and the Raman gain coefficient at 1.5 MPa of SF6 under the 532 nm pump laser was calculated to be 0.83 cm/GW by the SRS threshold comparison with H2. Using helium as the carrier gas, the thermal effect of the SF6 Raman laser was improved dramatically under a repetition rate of 10 Hz.
We demonstrate absorption spectroscopy of water vapor for the determination of gas temperature. An adaptive dual-comb detection system is utilized to obtain precise spectroscopic data in a broadband range from 7143 to 7240 cm?1 with a spectral resolution of 0.049 cm?1. The measured spectra are in accordance with the simulated results from the HITRAN (high-resolution transmission molecular absorption) database. Several measurements are investigated in the temperature range of 500–1000 K, revealing relative deviations of less than 5% compared to the thermocouple. This broadband and accurate adaptive dual-comb spectral detection method could be a powerful tool for non-invasive combustion diagnosis.
In recent years, multi-wavelength fiber lasers play a significant role in plenty of fields, ranging from optical communications to mechanical processing and laser biomedicine, owing to their high beam quality, low cost, and excellent heat dissipation properties. Benefitting from increasing maturity of optical elements, the multi-wavelength fiber laser has made rapid developments. In this review, we summarize and analyze diverse implementation methods covering continuous wave and pulsed fiber lasers at room temperature conditions: inserting an optical filter device and intensity-dependent loss structure in the resonant cavity, and applying ultrafast nonlinear optical response of materials and a dual-cavity structure. Finally, future challenges and perspectives of the multi-wavelength fiber laser are discussed and addressed.
The Laguerre–Gaussian (LG) mode beam has very important applications in many research fields. Here, the Theon sieve is first introduced into the laser resonator to generate petal-like laser beams by coherently superimposing two high-order LG modes. The effectiveness was verified by GLAD software. The petal-like laser beam is derived from the light field redistribution and coherent superposition caused by the diffraction effect of the Theon sieve. The relationship between the order of the petal-like laser and the cavity structures has also been investigated in detail. Light field operation in the laser cavity greatly simplifies the optical structure and is more beneficial to optical diagnostics and imaging.
For the first time, a group-VI single element nanomaterial was used as the optical saturable absorber (SA) to generate laser pulses. With two-dimensional (2D) tellurene as a passive Q-switch, 1.06 μm and 1.3 μm pulse laser operations were realized from a diode-pumped Nd:YAG crystal. The shortest pulse widths were 98 ns and 178 ns, and the highest peak powers were 2.68 W and 2.45 W, respectively. Our research determines that tellurene is an excellent SA material in the near-infrared region.
A deep convolutional neural network is employed to simultaneously measure the beam-pointing and phase difference of sub-beams from a single far-field interference fringe for coherent beam combining systems. The amplitudes of sub-beams in the measurement path are modulated in order to prevent measuring mistakes caused by the symmetry of beam-pointing. This method is able to measure beam-pointing and phase difference with an RMS accuracy of about 0.2 μrad and λ/250, respectively, in a two-beam coherent beam combining system.
A new disordered crystal Nd:SrAl12O19 (Nd:SRA) with an Nd3+ doping concentration of 5% was successfully grown using the Czochralski method. A diode-pumped Nd:SRA Q-switched laser operating at 1049 nm was demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. Based on an MXene Ti3C2Tx sheet, a high repetition rate of 201 kHz and a Q-switched pulse width of 346 ns were obtained when the absorbed pump power was 2.8 W. The peak power and single pulse energy were 1.87 W and 0.65 μJ, respectively.
The generation of mid-infrared pulsed lasers was achieved in a Ho3+:YAG laser pumped gain-switched Cr2+:CdSe laser system with the shortest pulse duration of 4.15 ns. With a pump pulse duration of 50 ns and pump power of 2.7 W, the gain-switched Cr2+:CdSe laser achieved over 10 times pulse narrowing, obtaining the maximum peak power of 5.7 kW. The optical-to-optical conversion efficiency was 3.7%, which could be further improved with better crystal surface polishing quality. The laser central wavelength was measured to be 2.65 μm with a bandwidth (FWHM) of 50 nm. In addition, the parameter optimization for suppressing the pulse tail was discussed, while the long cavity and high output transmissivity contributed to obtaining the single-peak pulses.
We demonstrated a femtosecond mode-locked Er:ZrF4-BaF2-LaF3-AlF3-NaF (Er:ZBLAN) fiber laser at 2.8 μm based on the nonlinear polarization rotation technique. The laser generated an average output power of 317 mW with a repetition rate of 107 MHz and pulse duration as short as 131 fs. To the best of our knowledge, this is the shortest pulse generated directly from a mid-infrared mode-locked Er:ZBLAN fiber laser to date. Numerical simulation and experimental results confirm that reducing the gain fiber length is an effective way to shorten the mode-locked pulse duration in the Er:ZBLAN fiber laser. The work takes an important step towards sub-100-fs mid-infrared pulse generation from mode-locked Er:ZBLAN fiber lasers.
We demonstrated a high-energy single-frequency erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Er:YAG) laser. With 1470 nm laser diodes (LDs) as pumping sources, single-frequency laser pulses with energy of 28.6 mJ, 21.6 mJ, and 15.0 mJ are obtained at pulse repetition frequency of 200 Hz, 300 Hz, and 500 Hz, respectively. As far as we know, this is the highest single-frequency pulse energy with the Er:YAG gain medium. With the ring cavity design, pulse duration is maintained at hundreds of nanoseconds. This high-energy single-frequency laser with hundreds of nanoseconds pulse duration is a prospective laser source for light detection and ranging applications.
The laser-induced damage threshold of a calcium fluoride (CaF2) single crystal was obtained by a 193 nm ArF excimer laser. The damage morphology of the crystal was analyzed. The results showed that the surface of CaF2 single crystal broke along the natural cleavage plane under ArF excimer laser irradiation, some fragments fell off, and Newton’s rings were observed on the curved fragments. Laser-induced periodic stripe structures (LIPSS) appeared on the surface layer beneath the fragments that peeled off. The spacing of LIPSS was measured, and the formation mechanism of LIPSS was analyzed based on the interference model.
High-power fiber-to-fiber coupling is extensively used in fiber laser applications, and its performance is determined by coupling efficiency. We demonstrate a novel method for alignment and monitoring efficiency by detecting backscattering power at the fiber end cap. The relationship between alignment error and backscattering power is determined by simulations and experiments. Through this method, a state-of-the-art kW-level fiber-to-fiber optic switch is developed (transmission efficiency >97%). It performs well for longer than 60 min. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time to establish the mathematical model based on this method. Our results can provide guidance in high-power fiber-to-fiber coupling.
A 1.5 J Nd:LuAG ceramic active mirror laser amplifier with a high beam quality is demonstrated in which a 0.8% (atomic fraction) Nd-doped Nd:LuAG ceramic disk with a diameter of 64 mm and a thickness of 5.5 mm is used as a laser gain medium. A maximum single-pass small-signal gain of 2.59 is measured when the pump energy is 11.5 J, with an injected seed energy of 0.4 J; a maximum output energy of 1.5 J is obtained at the repetition rate of 10 Hz. A far-field beam spot 1.25 times the diffraction limit (DL) is achieved by using a stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugation mirror (SBS-PCM) for wavefront correction.
Coherent beam combining of 60 fiber lasers by using the stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm has been demonstrated. The functions of pinhole(s) on the power distributions in the far-field have been systematically simulated on both in-phase and out-of-phase modes. Only one photoelectric detector was used to detect the combined power in the far-field central lobe of the in-phase mode state. When the phase controller was in a closed loop, the contrast of the far-field intensity pattern was as high as ~97% with residual phase error of ~λ/30, and ~34.7% of the total power was contained in the central lobe.
A 400 nm femtosecond laser was used to ablate the surface of a high-pressure and high-temperature diamond, and subwavelength surface micro structures with a period of 100 nm were achieved. A variety of micro-nano composite surface structures were prepared by changing the polarization direction and laser scanning direction. By dynamically adjusting the laser polarization and the laser scanning tracks, a maskless direct writing fabrication of micro-nano complex structures was realized. The micro-nano patterning on an ultra-hard and super-stabile diamond provides a new idea for the preparation of friction reducing surfaces, nano imprint transfer templates, surface enhanced Raman scattering test substrates, and micro-nano optical structures.
We report on laser diode (LD) pumped passively Q-switched Yb,Gd:SrF2 lasers with high single-pulse energy for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. In addition, a stable Q-switched laser based on a Cr4+:Y3Al5O12 saturable absorber was demonstrated. The maximum output power of the Q-switched laser obtained was 495 mW, with a pulse width and a pulse repetition rate of 233 ns and 1.238 kHz, respectively. The corresponding single-pulse energy and the peak power were as high as 400 μJ and 1.714 kW. The laser was operated under a transverse electromagnetic mode, and the beam quality was near-diffraction-limited.
A power-scaled laser operation of Pr:YLiF4 (YLF) crystal at 720.9 nm pumped by a 443.6 nm laser diode (LD) module was demonstrated. The 20 W module was used to pump the Pr:YLF crystal, and a maximum output power of 3.03 W with slope efficiency of 30.04% was obtained. In addition, a 5 W blue LD was also used to pump the Pr:YLF laser, and a maximum output power of 0.72 W was obtained at room temperature. The output power was limited by the wavelength mismatch between the single-emitter LD and the absorption peak of the crystal.
In this Letter, a novel system for adaptively correcting the phase of a dynamic multimode beam is proposed. While using merely one spatial light modulator, the phase measurement of the first-order diffraction pattern and the correction of the zeroth diffraction order are simultaneously realized. The real-time experimental result is obtained at a control rate of 10 Hz. The power-in-the-bucket value is improved from 38.5% to 61.8%, even with fundamental mode content that is consistently below 30%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first implementation of real-time adaptive correction of the entire multimode beam.
Aiming at the application requirements of information optics, this Letter proposed a perovskite quantum dot random lasing pumping method suitable for high-speed modulation. At the same time, the luminescence characteristics of perovskite quantum dot films under electron beam pumping conditions are analyzed, and the random lasing mechanism of electron beam pumping CsPbBr3 quantum dot films is revealed. Finally, it is confirmed that perovskite quantum dots are easy to realize random lasing under electron beam pumping conditions.
In this Letter, a dye-doped cholesteric liquid crystal (DDCLC)-filled hollow glass microsphere is demonstrated to be a resonator with good temperature response. A diglycerol layer is used to wrap the DDCLCs microdroplet to keep it steady and control its orientation. The whispering gallery mode (WGM) lasing and photonic band gap (PBG) lasing caused by two different mechanisms were obtained under the pump of a pulsed laser, and the temperature response of these two kinds of lasing was studied. For the liquid crystal and chiral material used in this Letter, both the WGM lasing and the PBG lasing have a blue shift in wavelength with increasing temperature.
Nd3+-doped fiber lasers at around 900 nm based on the 4F3/2 → 4I9/2 transition have obtained much research attention since they can be used as the laser sources for generating pure blue fiber lasers through the frequency doubling. Here, an all-fiber laser at 915 nm was realized by polarization-maintaining Nd3+-doped silica fiber. A net gain per unit length of up to 1.0 dB/cm at 915 nm was obtained from a 4.5 cm fiber, which to our best knowledge is the highest gain coefficient reported in this kind of silica fiber. The optical-to-optical conversion efficiency varies with the active fiber length and the reflectivity of the output fiber Bragg grating (FBG), presenting an optimal value of 5.3% at 5.1 cm fiber length and 70% reflectivity of the low reflection FBG. Additionally, the linear distributed Bragg reflector short cavity was constructed to explore its potential in realizing single-frequency 915 nm fiber laser. The measurement result of longitudinal-mode properties shows it is still multi-longitudinal mode laser operation with 40 mm laser cavity. These results indicate that the Nd3+-doped silica fiber could be used to realize all-fiber laser at 915 nm, which presents potential to be the seed source of high-power fiber laser.
We report here on a diode-pumped pulsed mid-infrared laser source based on gas-filled hollow-core fibers (HCFs) towards an all-fiber structure by the tapering method. The pump laser is coupled into an acetylene-filled HCF through a tapered single-mode fiber. By precisely tuning the wavelength of the diode to match different absorption lines of acetylene near 1.5 μm, mid-infrared emission around 3.1–3.2 μm is generated. With 2 m HCFs and 3 mbar acetylene gas, a maximum average power of 130 mW is obtained with a laser slope efficiency of ~24%. This work provides a potential scheme for all-fiber mid-infrared fiber gas lasers.
A dual-wavelength synchronously mode-locked homogeneously broadened bulk laser operating at 1985.6 and 1989 nm is presented for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, which delivers a maximum output power of 166 mW and a repetition rate of 85 MHz. The pulse duration was measured to be 16.8 ps by assuming a sech2 pulse shape. The recorded autocorrelation trace showed frequency beating signals with an interval of 3.8 ps and a full width at half-maximum duration of 2 ps, corresponding to an ultrahigh beating frequency of about 0.26 THz, which agrees well with the frequency difference of the emitted two spectral peaks. The results indicated that such a kind of dual-wavelength mode-locked Tm:YAlO3 laser could be potentially used for generating terahertz radiations.
Cylindrical shockwaves inside polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generated simultaneously with two hemispherical shockwaves induced by a femtosecond Gaussian beam laser were investigated using an ultrafast pump–probe imaging technique. The evolutions of these three shockwaves with probe delay and incident pulse number have been systematically analyzed. The plasma intensity and filament length in the center of cylindrical shockwave both decayed with pulse number. Moreover, the self-focused filament moved downstream towards the output surface with an increased pulse number. The experimental results and mechanism illustrated that energy deposition was suppressed by a degraded nonlinear effect due to a pre-ablated structure in multi-pulse irradiation.
We demonstrate a Fe:ZnSe laser gain-switched by a ZnGeP2 optical parametric oscillator (OPO) under the pulse repetition frequency of 1 kHz at room temperature. The 2.9 μm signal light of the OPO is employed as the pump for the Fe:ZnSe laser. The maximum output power of the Fe:ZnSe laser is 58 mW with the pulse duration of 2.7 ns under the incident pump power of 280 mW, corresponding to a peak pulse power of 21.5 kW and an optical-to-optical efficiency of 20.7%. The spectrum of the Fe:ZnSe laser has a range of 4030.2–4593.6 nm with a dip at 4187.1–4340.4 nm due to the absorption of CO2.
Excess frequency noise induced by mechanical vibration is the dominant noise source at low Fourier frequencies in fiber-delay-line stabilized lasers. To resolve this problem, a double-winding fiber spool is designed and implemented that has ultralow acceleration sensitivity in all spatial directions. By carefully choosing the optimal geometry parameters of the fiber spool, we achieve acceleration sensitivity of 8 × 10 11/g and 3 × 10 11/g (g denotes the gravitational acceleration) in axial and radial directions, respectively.
Spatio-temporal coupling characteristics of ultrafast laser pulses are quantitatively tailored. An asymmetric microstructure is induced in the focal volume when the laser scans perpendicularly to the direction of the spatial chirp in fused silica. The tilted direction reverses when adding a Dove prism into the light path. The sign of the pulse front tilt can be turned from positive to negative by changing the group delay dispersion by steps. We reveal that the tilted direction of a microstructure depends on spatial chirp, and the interplay between spatio-temporal chirp leads to the change of tilted angles.
Collinear phase-matching of sum-frequency generation (SFG) has been studied thoroughly previously, while non-collinear schemes are sometimes more flexible in application. However, this phase-matching type is more difficult to meet and control. We employ a convenient method to obtain harmonic generation in bulk potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP), using an incident wave vector and a reflected wave vector to create a triangle phase-matching relationship. With a simple, flexible set-up, we can observe 351 nm SFG, and the conversion efficiency is up to ~3.6% per reflection. Furthermore, we believe this approach has potential application value and improvement space.
We demonstrate the frequency stabilization of a 1.55 μm erbium-doped fiber laser by locking it to a 5-km-long optical fiber delay line (FDL). The stabilized laser is characterized via comparison with a second identical laser system. We obtain a fractional frequency stability of better than 3 × 10 15 over time scales of 1–10 s and a laser linewidth of 0.2 Hz, which is the narrowest linewidth of an FDL-stabilized laser observed to date.
Praseodymium-ion-doped gain materials have the superiority of lasing at various visible wavelengths directly. Simple and compact visible lasers are booming with the development of blue laser diodes in recent years. In this Letter, we demonstrate the watt-level red laser with a single blue laser diode and Pr:YLiF4 crystal. On this basis, the passively Q-switched pulse lasers are obtained with monolayer graphene and Co:ZnO thin film as the Q-switchers in the visible range.
High power laser diodes (LDs) with a lasing wavelength between 700 and 780 nm have great potential in various medical uses. Here, we report our recent efforts in developing an InGaAsP/AlGaInP-based commercial high power edge-emitting LD, which has 755 nm emission peak with a world-record continuous wave output power of 12.7 W, the highest reported so far. The lack of Al atoms in the active region significantly lowers the chance of catastrophic optical damage during high power laser operation. Meanwhile, with an accumulated 3800 h running time, our ongoing aging tests reveal excellent reliability of our devices.
With tin diselenide (SnSe2) film as a saturable absorber (SA), the passively Q-switched self-frequency doubling (SFD) lasers were realized in Nd3+:ReCa4O(BO3)3 (Re = Y, Gd) crystals. For Nd:YCa4O(BO3)3 crystal, the maximum average output power at 532 nm was 19.6 mW, and the corresponding pulse repetition frequency, pulse duration, single pulse energy, and peak power were 17.6 kHz, 91.9 ns, 1.1 μJ, and 12.1 W, respectively. For Nd:GdCa4O(BO3)3 crystal, these values were 14.5 mW, 22.1 kHz, 48.7 ns, 0.66 μJ, and 13.5 W.
We demonstrate here an environmentally stable and extremely compactable Er-doped fiber laser system capable of delivering sub-100-fs temporal duration and tens of nanojoules at a repetition rate of 10 MHz. This laser source employs a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror mode-locked soliton laser to generate seed pulses. A single-mode-fiber amplifier and a double-cladding-fiber amplifier (both with double-pass configuration) are bridged by a divider and used to manage the dispersion map and boost the soliton pulses. By using 64 replicas, pulses with as high as 60 nJ energy within 95 fs duration are obtained at 10 MHz, corresponding to 600 kW peak power.
A monolithic lens-window-prism (LWP) device, made of lithium fluoride (LiF) or magnesium fluoride (MgF2), was proposed. When either of the devices was fixed onto one end of a gas cell filled with Xe, it becomes a “wedge-crystal”-like device and was used to convert a 1 MHz femtosecond 347 nm laser to its third harmonic radiation at 10.7 eV. This led to an improved beam profile and a more compact and less lossy configuration. A stable output power of ~11 μW was demonstrated for 2 h using LiF-LWP. In addition, MgF2-LWP was also verified for its practicability at 10.7 eV.
An external frequency doubling electro-optically Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) 473 nm blue laser was demonstrated. With absorbed pump energy of 48 mJ at 100 Hz repetition rate, about 2 mJ of 473 nm blue laser pulse energy was achieved by cascade frequency doubling. The second harmonic conversion efficiency was 64.5%, and overall optical-optical efficiency was 4.2%, respectively. The blue laser pulse width was less than 10 ns, and beam quality factor was less than 2.4.
Space debris laser ranging was achieved with a 60 W, 200 Hz, 532 nm nanosecond slab, single-frequency green laser at the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory’s 60 cm satellite laser ranging system. There were 174 passes of space debris measured in 2017, with the minimum radar cross section (RCS) being 0.25 m2 and the highest ranging precision up to 13.6 cm. The RCS of space debris measured with the farthest distances in 174 passes was analyzed. The results show that the farthest measurement distance (R) and RCS (S) were fitted to R = 1388.159S0.24312, indicating that this laser can measure the distance of 1388.159 km at an RCS of 1 m2, which is very helpful to surveillance and research on low-Earth-orbit space debris.
In this Letter, a 116-actuator deformable mirror (DM) was used to correct the wavefront distortion in a 10.7 J, 10 Hz neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) slab amplifier. By applying a pump-light homogenizer to transform the 3 × 1 near-field beam array into an integrated beam, the beam quality was greatly improved from 5.54 times diffraction limit (TDL) to 1.57 TDL after being corrected by the DM. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first investigation on beam quality control of an arrayed near-field beam in high-energy diode-pumped solid-state lasers.
The excitation of high-order Laguerre–Gaussian (LG) modes in a neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser resonator was presented by applying the diffraction of a second-order circular Dammann grating (CDG) for annular pumping. In the study, the 808 nm pump light was shaped into a double-ring structure by the CDG and matched spatially with that of an ideal LG11 mode. As a result, the laser resonator generated an LG11 vortex mode, and the laser power reached 204 mW with 14.5% slope efficiency. Also, when the cavity mirror was tilted, the laser output could switch to the LG01 vortex mode. The results showed the convenience and versatility of CDG in an annular-pumped vortex laser.
A saturable absorber is commonly employed to generate an ultrashort laser with a mode-locking scheme. In an erbium-doped fiber laser system, the laser regimes of either 1530 or 1550 nm wavelength are procured based on the absorption profile of the erbium-doped fiber. The absorption of the erbium-doped fiber is designed to emit at both wavelengths by controlling the net gain of the laser cavity. Subsequently, simultaneous erbium-doped fiber laser emission is attained at 1533.5 and 1555.1 nm with the pulse duration of 910 and 850 fs, respectively. Therefore, this work maximizes the output portfolios of a mode-locking fiber laser for dual-wavelength ultrashort pulses emission.
We report a hybrid femtosecond laser system based on a femtosecond Yb-doped fiber laser and a Yb-doped potassium gadolinium tungstate (Yb:KGW) regenerative amplifier. To match the central wavelength of the seed source, a Yb:KGW crystal is used in the regenerative amplifier for Np polarization. We study and optimize the dynamics of nonlinear amplification to alleviate the gain narrowing effect. With optimization, the system can output 270 fs pulses with 21 μJ pulse energy at a 60 kHz repetition rate.
We demonstrate a coherent synthesis system based on femtosecond Yb-doped fiber laser technology. The output pulse of the amplification system is divided into two replicas and seeded into photonic crystal fibers of two parallel branches for nonlinear pulse compression. Because of the different nonlinear dynamics in the photonic crystal fibers, the compressed pulses show different spectra, which can be spliced to form a broad coherent spectrum. The integrated timing jitter between the pulses of two branches is less than one tenth of an optical cycle. By coherently synthesizing pulses from these two branches, 8 fs few-cycle pulses are produced.
We demonstrate a 0.95 GHz repetition rate fully stabilized Yb:fiber frequency comb without optical amplification. Benefitting from the high mode power and high coherence, this comb achieved 35 to 42 dB signal to noise ratio on the direct heterodyne beat signals with at least six continuous wave lasers (at 580, 679, 698, 707, 813, and 922 nm) while keeping >40 dB carrier envelope frequency signal. It can be used for the direct measurement of optical frequencies at visible and near-infrared wavelengths and has great potential on simultaneous comparison of multiple optical frequencies.
Gold nanorods (GNRs) with two different aspect ratios were successfully utilized as saturable absorbers (SAs) in a passively Q-switched neodymium-doped lutetium lithium fluoride (Nd:LLF) laser emitting at 1.34 μm. Based on the GNRs with an aspect ratio of five, a maximum output power of 1.432 W was achieved, and the narrowest pulse width was 328 ns with a repetition rate of 200 kHz. But, in the case of the GNRs with the aspect ratio of eight, a maximum output power of 1.247 W was achieved, and the narrowest pulse width was 271 ns with a repetition rate of 218 kHz. Our experimental results reveal that the aspect ratios of GNRs have different saturable absorption effects at a specific wavelength. In other words, for passively Q-switched lasers at a given wavelength, we are able to select the most suitable GNRs as an SA by changing their aspect ratio.
The spatial resolved method, which measures the laser-induced damage fluence by identifying the location of the damage point in the Gaussian beam three-dimensional direction, is demonstrated. The advantages and practicality of this method have been explained. Taking a triple frequency beam splitter as an example, the defect damage fluence can be accurately calculated by the spatial resolved method. The different defect damage performance of the triple frequency splitter is distinguished under irradiations of only the 355 and 532 nm lasers. The spatial resolved method provides a way to obtain precise information of optical film defect information.
A novel 1 kHz single-frequency, Q-switched Er-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Er:YAG) laser pumped by a 1470 nm laser diode is demonstrated. The 500 ns, 5.52 mJ single-frequency, diffraction-limited pulses are obtained by using a ‘ramp-fire’ injection-seeding technique and an optical feedback architecture. The full width at half-maximum of the pulse spectrum is measured to be 1.47 MHz by using the heterodyne technique. The beam quality M2 factors are measured to be 1.18 and 1.24 in the x and y directions, respectively.
In this work, non-isothermal bleaching of Yb–Li co-doped fiber was investigated. The Yb–Li co-doped fiber was beneficial to reduce the photodarkening-induced excess loss and had no bad effect on the temperature of thermal bleaching (TB). Photodarkened fibers were bleached with different temperature ramp rates. The higher the ramp rate, the higher the complete bleaching temperature. The activation energy of the bleaching of Yb/Al/Li fiber was calculated by fitting, which was similar to that of an Yb-doped fiber. These observations are helpful in revealing the relationship between the mechanism of Li ion co-doping and TB.
Experimental generation of stable mode-locked pulses and cylindrical vector beams (CVBs), from an all few-mode fiber (FMF) ring laser is first reported, to the best of our knowledge. In this laser, a section of few-mode erbium-doped fiber (FM-EDF) is used as the gain medium. The FM-EDF is pumped by 976 nm laser with LP11 mode, which is simultaneously converted and multiplexed through a homemade hybrid device, i.e., wavelength division multiplexing-mode selection coupler (WDM-MSC). All the components in our experiment are connected using FMF. The resulted CVB pulses have a spectral width of 0.33 nm with a repetition rate of 30.58 MHz under the pump power of 340 mW. Moreover, both azimuthally and radially polarized CVBs were achieved with a high purity of >95%. This mode-locked CVB fiber laser with an all FMF configuration opens the way to manipulate the transverse mode in mode-locked fiber lasers.
Due to the composition-dependent properties of two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), alloying of existing dissimilar TMDs architecture is a novel and controllable route to tailor crystal structures with superior optical and optoelectronic properties. Here, we reported the hexagonal-phase WSe1.4Te0.6 alloy can enable great promise for enhanced saturable absorption response exceeding the parent component WSe2 and WTe2, with larger modulation depth and lower saturable intensity. These advantages allowed the 1064 nm passively Q-switched lasers based on WSe1.4Te0.6 to be more efficient, with pulse duration narrowed to 45%, and slope efficiency increased by 232%. Our findings highlighted the appropriate alloying of TMDs as an effective strategy for development of saturable absorbers.
Fifth harmonic generation (5th HG) of a Nd:glass laser is an effective way to acquire high-energy coherent deep-ultraviolet radiation near 200 nm. In this work, cascade generation of the fifth harmonic of a Nd:glass laser in a 5 mm ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) crystal was investigated, and maximum conversion efficiency of 14% and large angular acceptance of 45 mrad were demonstrated at a noncritical phase-matching temperature of 75.1°C. However, as the results reveal, the temperature sensitivity and nonlinear absorption would hinder its high-energy application. As for that, based on the complementary relationship of the angle and temperature in the phase-matching condition, an upgraded focusing 5th HG design coupled with the cylindrical temperature distribution scheme was proposed. By this upgraded focusing design, more than the improvement of the conversion efficiency, the output 5ω near-field intensity distribution turns out to be insensitive to the temperature gradient. Potentially, this idea can be applied for many other frequency conversion schemes such as high-repetition frequency lasers, which have similar temperature gradient problems.
We report an efficient mid-infrared extracavity optical parametric oscillator (OPO) based on the nonlinear crystal BaGa4Se7 pumped by a diode-side-pumped Q-switched Nd:Y3Al5O12 (Nd:YAG) laser. The maximum pulse energy of 1.03 mJ at 4.25 μm is obtained with the repetition rate of 10 Hz and pulse width of 12.6 ns when the pump energy was 13.5 mJ, corresponding to an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 7.6% from 1.064 μm to 4.25 μm. The idler wave slope conversion efficiency was 12%. To the best of our knowledge, it is the highest reported conversion efficiency for the compact BaGa4Se7 OPO driven by the Nd:YAG laser.
We demonstrate an effective approach of mode suppression by simply using a tungsten probe to destroy the external neck surface of polymer microbottle resonators. The higher-order bottle modes with large axial orders, spatially located around the neck surface of the microresonator, will suffer large optical losses. Thus, excitation just with an ordinary free-space light beam will ensure direct generation of single fundamental bottle mode lasers. This method is with very low cost and convenient and can obtain high side-mode suppression factors. Our work demonstrated here may have promising applications such as in lasing and sensing devices.
A laser diode partially end-pumped, electro-optically Q-switched, Yb:Y3Al5O12 (Yb:YAG) slab laser was reported. We obtained output energy of 14.6 mJ/pulse with a pulse width of 30 ns at a repetition frequency of 2 kHz, and the corresponding peak power was 480 kW. The beam quality factors M2 in the unstable direction and the stable direction was 1.32 and 1.25, respectively.
We examined a 1514 nm eye-safe passively Q-switched self-optical parametric oscillator. The nonlinear crystal is an a-cut Nd:MgO:PPLN crystal, and the size of the crystal was 6 mm × 2 mm × 30 mm with 0.4 at.% Nd3+ doped and a grating period of 29.8 μm. When the crystal absorbed 12.8 W, the output maximum single-pulse energy reached 39 μJ, and a pulse width of 6.1 ns at a repetition rate of 5.4 kHz was obtained. The peak power was 6 kW, giving a slope efficiency of 42%.
With a Nd:ScYSiO5 crystal, a high peak power electro-optically Q-switched 1.0 μm laser and tri-wavelength laser operations at the 1.3 μm band are both investigated. With a rubidium titanyle phosphate (RTP) electro-optical switcher and a polarization beam splitter, a high signal-to-noise ratio 1.0 μm laser is obtained, generating a shortest pulse width of 30 ns, a highest pulse energy of 0.765 mJ, and a maximum peak power of 25.5 kW, respectively. The laser mode at the highest laser energy level is the TEM00 mode with the M2 value in the X and Y directions to be Mx2 = 1.52 and My2 = 1.54. A tri-wavelength Nd:ScYSiO5 crystal laser at 1.3 μm is also investigated. A maximum tri-wavelength output power is 1.03 W under the absorbed pump power of 7 W, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 14.8%. The properties of the output wavelength are fully studied under different absorbed pump power.
We report a distributed-Bragg-reflectors-based 4 × 40 GHz mode-locked laser diode (MLLD) array monolithically integrated with a multimode interference (MMI) combiner. The laser produces 2.98 ps pulses with a time-bandwidth product of 0.39. The peak wavelength of the MLLD array can be tuned by 8.4 nm while maintaining a good mode-locked state. The four mode-locked channels could work simultaneously with the peak wavelength interval around 3 nm.
In this Letter, we demonstrate high-quality (Q), millimeter-size, and V-shaped calcium fluoride crystalline resonators for modal modification. To manufacture such resonators, we develop a home-made machining system and explore a detailed process. With a dedicated polished container, three special polishing steps, including grinding, smoothing, and polishing, are employed to achieve the required surface smoothness, which is characterized by less than 3 nm. An ultra-high-Q factor exceeding 108 is obtained by a coupled tapered fiber. In addition, a customized packaged structure for our disk resonator is achieved. The Q maintenance and stable spectrum are realized by sealing the coupling system in a hard disk. The simple, stable, portable, controlled, and integratable device would provide great potential in optical filters, sensors, nonlinear optics, cavity quantum electrodynamics, and especially some applications that require large resonators such as gyroscopes.
Particle ejection is an important process during laser-induced exit surface damage in fused silica. Huge quantities of ejected particles, large ejection velocity, and long ejection duration make this phenomenon difficult to be directly observed. An in situ two-frame shadowgraphy system combined with a digital particle recognition algorithm was employed to capture the transient ejecting images and obtain the particle parameters. The experimental system is based on the principle of polarization splitting and can capture two images at each damage event. By combining multiple similar damage events at different time delays, the timeline of ejecting evolution can be obtained. Particle recognition is achieved by an adaptively regularized kernel-based fuzzy C-means algorithm based on a grey wolf optimizer. This algorithm overcomes the shortcoming of the adaptively regularized kernel-based fuzzy C-means algorithm easily falling into the local optimum and can resist strong image noises, including diffraction pattern, laser speckle, and motion artifact. This system is able to capture particles ejected after 600 ns with a time resolution of 6 ns and spatial resolution better than 5 μm under the particle recognition accuracy of 100%.
Using a heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber prepared by the sol-gel method combined with high temperature sintering, the temperature dependence of the spectrum around the 1.55 nm band and single-mode fiber laser properties were investigated, respectively. The absorption cross section increases 29.2% at ~1558 nm with the temperature increasing from 20°C to 140°C, while the emission cross section slightly increases 4.3%. In addition, the laser slope of the heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber at 1558 nm decreases 4.4% from 10.8% to 6.4% with the temperature increasing from 18°C to 440°C. Meanwhile, an experiment lasting 3 h proves that the fiber laser has excellent stability below 440°C.
This study investigates the applicability of a few-layer structure ReSe2 as a saturable absorber (SA) for demonstrating a passively Q-switched pulse laser. The ReSe2 SA had a modulation depth of 6.86%. The Q-switched experiment was successful in delivering a maximum average output power of 180 mW at the wavelength of 1906.5 nm. The optimal pulse train had a pulse width of 1.61 μs and a repetition rate of 28.78 kHz. The experiment results verify that the few-layer structure ReSe2 could behave as an excellent SA at all-solid-state lasers, increasing the selection of SAs at near 2 μm lasers.
A modified spectral beam combining (SBC) approach based on double asymmetrical filters was proposed. By using this scheme, the high-order lateral modes at the edge of the far-field pattern can be suppressed in the external cavity, and the beam quality in the slow-axis direction was improved from 16.1 to 13.4 compared to the conventional SBC. In the meanwhile, the electrical-to-optical efficiency from the modified SBC was more than 40% with an output power of 34.1 W, which is similar to that of the conventional SBC.
The ablation of sintered silicon carbide ceramics by an ArF excimer laser was studied. Three zones are generated: the ablation zone that presented molten morphology and was composed by the Si and C phase; the condensation zone formed by vaporized SiC; and the oxidation zone that showed the characteristics of thermal oxidation. The ablation depth and oxidation range increase linearly with fluence and pulses within 0.5–4 J/cm2, but the normalized ablation efficiency is constant (3.60 ± 0.60 μm·mm2/J). The theoretical photochemical ablation depth supplies 25% of the total depth at 1 J/cm2 but decreases to 16% at 4 J/cm2. The ablation is dominated by the photothermal effect and conforms to the thermal evaporation mechanism.
We report 20 Gb/s transmission of four-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) signal using a directly modulated tunable distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser. Transmission distance over 20 km was achieved without using optical amplifiers and optical dispersion compensation modules. A wavelength tuning range of 11.5 nm and a 3 dB bandwidth greater than 10 GHz over the entire wavelength tuning range were obtained.
Few-layer graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets were fabricated and utilized as a saturable absorber for mode-locking in an Er-doped fiber laser with net normal dispersion. The g-C3N4/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hybrid-film-based saturable absorber has a modulation depth of 4.01% and a saturation intensity of 7.5 MW/cm2. By integrating g-C3N4-PVA mode-locker into the laser cavity, a mode-locked operation could be obtained. The achieved mode-locking pulse centered at 1530.3 nm has a pulse width of 530 ps. Its repetition rate is 40.8 MHz, and the corresponding signal-to-noise ratio is about 55 dB.
Microlasers based on high quality (Q) whispering-gallery mode (WGM) resonance are promising low threshold laser sources for bio-sensing and imaging applications. In this Letter, dye-doped polymer microspheres were fabricated by a controlling emulsion solvent evaporation method. WGM lasing with low threshold and high Q factors was realized in an individual microsphere under femtosecond laser pumping. The slight change of environmental relative humidity (RH) can be monitored by measuring the shift of the lasing modes at the exposure of water molecules, which demonstrates the sensitivity is as high as 6 pm/RH%. The results would offer an insight into employing microlasers as sensors.
We proposed a novel wavelength-spread compression technique for spectral beam combining of a diode laser array. A reflector, which is parallel to the grating, is introduced to achieve a double pass with a single grating. This facilitated the reduction of the wavelength spread by half and doubled the number of combined elements in the gain range of the diode laser. We achieved a power of 26.1 W under continuous wave operation using a 19 element single bar with a wavelength spread of 6.3 nm, which is nearly half of the original wavelength spread of 14.2 nm, demonstrating the double-compressed spectrum capability of this structure. The spectral beam combining efficiency was 63.7%. The grating efficiency and reflector reflectance were both over 95%; hence, the efficiency loss of the double-pass grating with a reflector is acceptable. In contrast to double-grating methods, the proposed method introduces a reflector that efficiently uses the single grating and shows significant potential for a more efficient spectral beam combining of diode laser arrays.
A Ti:sapphire crystal with a diameter of 235 mm and thickness of 72 mm was grown by the heat exchange method (HEM). The absorption intensity of the crystal at 532 nm averaged at 91%. The figures of merit (FOMs) at different positions of the crystal were measured and the FOM value in the central region was found to reach 90. The transmittance laser beam was intact with no obvious distortions and had only a small deformation compared with the incident laser beam. A small-signal amplification experiment was performed on the Ti:sapphire crystal and a gain of more than 6 times was achieved with a pump energy density of 1.98 J/cm2. These tests indicate that the 235 mm Ti:sapphire crystal has excellent optical qualities and will further improve the energy output of a 10 PW laser system.
We demonstrate a femtosecond Cr:YAG laser mode-locked by a carbon nanotube saturable absorber mirror (CNT-SAM) at a repetition rate of 550 MHz. By employing the CNT-SAM, which exhibits a modulation depth of 0.51% and a saturation fluence of 28 μJ/cm2 at 1.5 μm, we achieved a compact bulk Cr:YAG laser with self-starting mode-locked operation near 1.5 μm, delivering an average output power of up to 147 mW and a pulse duration of 110 fs. To our knowledge, this system provides the highest repetition rate among reported CNT-SAM mode-locked Cr:YAG lasers and the shortest pulse duration among saturable absorber mode-locked Cr:YAG lasers with repetition rates above 500 MHz.
Sub-picosecond chirped laser pulse-induced airflow and water condensation were investigated in a cloud chamber. The results indicate that the positively chirped sub-picosecond laser pulses generate a more uniform intensity distribution inside the plasma column, leading to a weaker airflow and an elliptic-shaped snow pile. The negatively chirped sub-picosecond laser pulses generate a spark-like intensity distribution inside the plasma column, which produces a wider range of airflow and a round snow pile. The amount of snow weight and the concentration of NO3 are found to be dependent on the intensity distribution inside the plasma column. The visibly stronger plasma column generates much more snow and a higher concentration of NO3 . These experimental results provide a reference for sub-picosecond laser-induced water condensation in realistic atmospheric conditions.
A high power linearly polarized tunable Raman random fiber laser (RFL) was studied theoretically and experimentally. The parameters required for the system design were obtained through numerical simulation, based on which a hundred-watt-level linearly polarized tunable RFL was successfully demonstrated. The central wavelength can be continuously tuned from 1113.76 to 1137.44 nm, and the output power exceeds 100 W for all of the lasing wavelengths with the polarization extinction ratio (PER) exceeding 20 dB at the maximum output power. Besides, the linewidth, spectral evolution, and temporal dynamics of a specified wavelength (1124.72 nm) were investigated in detail. Moreover, the theoretical results and the experimental results fit well. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time for a hundred-watt-level linearly polarized tunable RFL ever reported.
Dissimilar metal joining of magnesium to aluminum was investigated using the latest generation nanosecond pulsed fiber laser. The tensile shear test shows that the average tensile shear strength of a joint was 86 MPa, which was 75% of the aluminum substrate. The weld interface exhibited a mixture phase (Mg solid solution and Mg17Al12) that improves the strength and toughness of the joint. A thin Mg–Al intermetallic compound layer was formed on both sides of the weld seam toward the Al side. Fracture occurred toward the Al substrate side rather than the Mg–Al interface, indicating a high joining strength at the weld interface.
A clock laser based on a 30-cm-long ultrahigh finesse optical cavity was developed to improve the frequency stability of the Sr optical lattice clock at the National Institute of Metrology. Using this clock laser to probe the spin-polarized Sr87 atoms, a Rabi transition linewidth of 1.8 Hz was obtained with 500 ms interrogation time. Two independent digital servos are used to alternatively lock the clock laser to the S01 (mF=+9/2)→P03 (mF=+9/2) transition. The Allan deviation shows that the short-term frequency stability is better than 3.2×10 16 and averages down followed by 1.8×10 15/τ.
Tm:CaF2 and Tm,Y:CaF2 single crystals were prepared by the temperature gradient technique. The spectral properties of Tm,Y:CaF2 single crystals were investigated and compared with those of Tm:CaF2. It was demonstrated that codoping with Y3+ ions could efficiently improve the spectroscopic properties. Tm,Y:CaF2 crystals have larger absorption cross-sections at the pumping wavelength, larger mid-infrared stimulated emission cross-sections, and much longer fluorescence lifetimes of the upper laser level (Tm3+: H43 level) than Tm:CaF2 crystals. Continuous-wave (CW) lasers around 1.97 μm were demonstrated in 4.0 at. % Tm,4.0 at. % Y:CaF2 single crystals under 792 nm laser diode (LD) pumping. The best laser performance has been demonstrated with a low threshold of 0.368 W, a high slope efficiency of 54.8%, and a maximum output power of 1.013 W.
To reveal the physical mechanism of laser ablation and establish the prediction model for figuring the surface of fused silica, a multi-physical transient numerical model coupled with heat transfer and fluid flow was developed under pulsed CO2 laser irradiation. The model employed various heat transfer and hydrodynamic boundary and thermomechanical properties for assisting the understanding of the contributions of Marangoni convention, gravitational force, vaporization recoil pressure, and capillary force in the process of laser ablation and better prediction of laser processing. Simulation results indicated that the vaporization recoil pressure dominated the formation of the final ablation profile. The ablation depth increased exponentially with pulse duration and linearly with laser energy after homogenous evaporation. The model was validated by experimental data of pulse CO2 laser ablation of fused silica. To further investigate laser beam figuring, local ablation by varying the overlap rate and laser energy was conducted, achieving down to 4 nm homogenous ablation depth.
With the increasing output power of the monolithic fiber laser oscillators, the stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) effect becomes one of the main limitations of power scaling. Employing fiber with a larger mode area is an effective technique to mitigate the SRS, but, for the monolithic fiber laser oscillators, the difficulty of the inscription of the high-reflection fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) increases with the fiber mode area. In this work, we demonstrated a high-power monolithic fiber laser oscillator based on the home-made large mode area FBGs and ytterbium-doped fiber (YDF) with 25 μm core diameters. A maximum output power of 4.05 kW is achieved at the central wavelength of ~1080 nm with a total 915 nm pump power of ~6.7 kW. At the operation of 4.05 kW, the intensity of the Raman Stokes light is ~25 dB below the signal laser, and the beam quality (M2-factor) is ~2.2. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first detailed report of the monolithic fiber laser oscillator with an output power beyond 4 kW.
Ellipsometry is a powerful and well-established optical technique used in the characterization of materials. It works by combining the components of elliptically polarized light in order to draw information about the optical system. We propose an ellipsometric experimental set-up to study polarization interference in the total internal reflection regime for Gaussian laser beams. The relative phase between orthogonal states can be measured as a power oscillation of the optical beam transmitted through a dielectric block, and the orthogonal components are then mixed by a polarizer. We show under which conditions the plane wave analysis is valid, and when the power oscillation can be optimized to reproduce a full pattern of oscillation and to simulate quarter- and half-wave plates.
We propose and simulate a method for generating a three-dimensional (3D) optical cage in the vicinity of focus by focusing a double-ring shaped radially and azimuthally polarized beam. Our study shows that the combination of an inner ring with an azimuthally polarized field and an outer ring with a radially polarized field and a phase factor can produce an optical cage with a dark region enclosed by higher intensity. The shape of the cage can be tailored by appropriately adjusting the parameters of double-mode beams. Furthermore, multiple 3D optical cages can be realized by applying the shift theorem of the Fourier transform and macro-pixel sampling algorithm to a double-ring shaped radially and azimuthally polarized beam.
A self-starting simple structured dual-wavelength passively mode-locked (ML) erbium-doped fiber (EDF) laser is proposed in this Letter. An all-fiber ring cavity is adopted and a transmission-type semiconductor saturable absorber is used as modelocker. In this laser, there are two gain humps located at the 1530 nm region and the 1550 nm region, respectively. Along with the length of EDF increasing, the intensity of the hump at 1530 nm region is gradually suppressed because of the re-absorption of emission by the ground state. With the proper length of EDF, the gain intensities of two regions are very close. When the pump power is above the ML threshold, the self-starting dual-wavelength ML operation is achieved easily without manual adjustment. The two spectral peaks with close intensities are located at 1532 and 1552 nm, respectively. The effect of intracavity dispersion on the output spectrum is also experimentally demonstrated.
We propose, design, and realize a compact stabilized laser system that can be tuned within 24 GHz automatically. This laser system consists of two distributed feedback (DFB) lasers, one of which is reference and locked to the D2 line of Rb87, the other laser is a slave that is locked to the reference laser via a loop servo. We measured the frequency of the beating signal of the two lasers and generated an error signal, which controlled the frequency of the slave laser to close the loop. We compressed the fluctuation of the beating signal’s frequency to less than 1 MHz. Furthermore, the system can also automatically determine and control whether the slave is red detuned or blue detuned to the reference. The dimensions of our laser system are about 15 cm × 20 cm × 10 cm. This kind of laser system can be applied in many important applications, such as atomic interferometer and cold atomic clock.
We report a double Q-switched 946 nm laser with a magnesium-oxide-doped LiNbO3 (MgO:LN) electro-optic (EO) crystal and a monolayer molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) saturable absorber (SA). A pulsed laser diode side-pumped long neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet rod (φ3×65 mm) is used as the gain medium. Large pulse energy up to 3.15 mJ and peak power up to 346 kW are generated at the repetition rate of 550 Hz, corresponding to the beam quality factors of Mx2=3.849, My2=3.868. Monolayer MoSe2 nanosheets applied in the experiment would be a promising SA for a passive Q-switching operation.
A simple technique is proposed for highly-efficient plane processing fully based on femtosecond laser beam shaping. The laser intensity distribution is transformed from a Gaussian to a donut shape. As the donut-shaped focus seems like a flat top from the side view, a plane with a high level of flatness is obtained directly by scanning once. By applying it to polishing experiments, the surface roughness can be improved significantly. The influence of scanning speed, laser pulse energy, and scanning times on the roughness is also discussed. Moreover, the scanning width can be flexibly controlled in a wide range.
The interest in tunable ultrafast fiber lasers operating in the 1.3 μm region has seen a significant increase due to rising demands for bandwidth as well as the zero-dispersion characteristic of silica fibers in this wavelength region. In this work, a tunable mode-locked praseodymium-doped fluoride fiber (PDFF) laser using single-walled carbon nanotubes as a saturable absorber is demonstrated. The mode-locked pulses are generated at a central wavelength of 1302 nm with a pulse repetition rate of 5.92 MHz and pulse width of 1.13 ps. The tunability of the mode-locked PDFF laser covers a tuning range of 11 nm.
In this Letter, we report on a novel architecture for a self-starting mode-locked figure-eight erbium-doped fiber laser using a loss-imbalanced nonlinear optical loop mirror (NOLM) with a bidirectional output coupler. An all-polarization-maintaining structure is adopted. A 2 × 2 optical coupler with a splitting ratio of 50:50 is used at the junction to form an NOLM. Another coupler with a splitting ratio of 10:90 is introduced at one end of the fiber loop. The 10:90 coupler plays two roles: power attenuator and bidirectional output coupler. This architecture can achieve both large modulation depth and good self-starting ability simultaneously. With this architecture, the self-starting mode-locking operation is achieved easily with pump power above the threshold. The clockwise and counter-clockwise mode-locked output powers are 10.1 and 10.3 mW, respectively, with the repetition rate of 3.63 MHz. The spectral bandwidths of the clockwise and counter-clockwise mode-locked output pulses are 7.4 and 2.9 nm, and the corresponding pulse widths of the direct outputs are 530.6 fs and 1.55 ps, respectively.
We demonstrate a proposal for making an ultrastable laser referenced to a multi-cavity, enabling a lower thermal noise limit due to the averaging effect. In comparison with a single-cavity system, relative frequency instability of the synthesized laser can be improved by a factor of the square root of the cavity number. We perform an experiment to simulate a two-cavity system with two independent ultrastable lasers. Experimental results show that the relative frequency instability (Allan deviation) of the synthesized laser is 5 × 10 16, improved by a factor of √2 from a single-cavity-stabilized laser.
A high-beam-quality diode-pumped neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) active mirror laser amplifier was demonstrated. The size of the Nd:YAG crystal was 48 mm × 42 mm × 11 mm with 0.6 at.% Nd doped. When the pump energy was 26.8 J and the input energy was 0.3 J, the output pulse energy reached 5.4 J, and the pulse width of 11.3 ns at a 5 Hz repetition rate was obtained for the two gain modules in three-pass amplification, with corresponding optical-to-optical efficiency of 21.2%. The beam quality was measured as Mx2=2.48 and My2=2.43 in horizontal and vertical directions, respectively.
Impact and torsion pendulums are applied in impulse coupling experiments of high-energy laser irradiation of space debris. It is difficult to achieve a multi-pulse experiment and thus hard to analyze the multi-pulse impulse coupling effect. Here, we designed a new recoil impulse experimental measurement system of non-contact, multi-degrees of freedom, and multi-pulse irradiation. The system used a low-pressure and low-temperature vacuum chamber to simulate the space environment, the pinning effect of magnetic levitation to achieve aluminum target suspension, and high-speed cameras to record the displacement over time to calculate the impulse of the target. Then the impulse coupling experiment of multi-pulse laser irradiation on the aluminum target was performed. The result shows that the multi-pulse impulse coupling effect is not the linear accumulation of coupling results by every single-pulse and multi-pulse coefficient that decreases with the increase of the number of pulses, and eventually stabilizes as the decrease gets smaller.
44.6 fs pulses from a 257 MHz, mode-locked non-polarization maintaining Er-doped fiber laser based on a biased nonlinear amplifying loop mirror are reported. The output power is 104 mW and the single-pulse energy is 0.4 nJ. The minimum pulse duration of the direct output is 44.6 fs, which is the shortest in this kind of laser.
In order to improve the morphology of microchannels fabricated by femtosecond laser ablation, the thermal process was introduced into the post-treatment processing. It was found that the thermal process cannot only decrease the roughness but also the width and depth of the microchannel. The change rates of width, depth, and roughness of the microchannel increase with processing temperature. When we prolong the time of constant temperature, the change rate of the width decreases at the beginning, and then it tends to be stable. However, the change rates of depth and roughness increase, and then they tend to be stable. In this Letter, we discuss the reasons of the above phenomena.
We demonstrate a high-efficiency and high-power quasi-three-level laser based on a trapezoidal composite slab architecture with a 270 μm-thick Yb-doping surface. The design of a surface-doped slab architecture, temperature effects, laser oscillator model, and laser oscillator experiments with a surface-doped slab as a laser host medium have been presented. By theoretical calculation, the temperature rise in the surface-doped slab is only one seventh of that in the bulk-doped slab at the same maximum pump power of 30 kW. Finally, in the laser oscillator experiments, an output energy of 21.6 J is obtained when the pump energy is 48 J with a repetition rate of 5 Hz and a pulse width of 1 ms. The optical-optical efficiency is 45%.
The stress damage process of a single crystal silicon wafer under millisecond laser irradiation is studied by experiments and numerical simulations. The formation process of low-quality surface is monitored in real-time. Stress damage can be observed both in laser-on and -off periods. Plastic deformation is responsible for the first stress damage in the laser-on period. The second stress damage in the laser-off period is a combination of plastic deformation and fracture, where the fundamental cause lies in the residual molten silicon in the ablation hole.
A solid-state green-light-emitting upconversion coherent random laser was realized by pumping macroporous erbium-doped lithium niobate with a 980 nm laser. The lasing threshold was determined to be about 40 kW/cm2. Above the threshold, the emission intensity increased sharply with the increasing pump intensity. Moreover, a narrow multi-peaks structure was observed in the green-light-emission band, and the positions of lasing lines were various at different angles. The results were the direct evidences of coherent random lasing emission from macroporous erbium-doped lithium niobate. These phenomena were attributed to the coexistence of upconversion emission and a multiple scattering feedback mechanism.
In this Letter, the loss and gain characteristics of an unconventional InxGa1 xAs/GaAs asymmetrical step well structure consisting of variable indium contents of InxGa1 xAs materials are measured and analyzed for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. This special well structure is formed based on the indium-rich effect from the material growth process. The loss and gain are obtained by optical pumping and photoluminescence (PL) spectrum measurement at dual facets of an edge-emitting device. Unlike conventional quasi-rectangle wells, the asymmetrical step well may lead to a hybrid strain configuration containing both compressive and tensile strains and, thus, special loss and gain characteristics. The results will be very helpful in the development of multiple wavelength InGaAs-based semiconductor lasers.
We evaluate the effects of the holes geometry drilled by a femtosecond laser on a stainless alloy with various defocused irradiation time, which ranges from 0 min to 1 h. The laser ablation efficiency is increased by a factor of 3 when the irradiation time is elevated from 0 to 30 min. Also, the morphology of the hole is observed by a scanning electron microscope, where the result indicates that the defocused irradiation time has a significant influence on the morphology changes. The reason for such changes is discussed based on the pretreatment effect and the confined plasma plume. As an application example, the microchannel is fabricated by a femtosecond laser combined with the defocused irradiation to demonstrate the advantage of the proposed method in fabricating functional structures.
We propose a nonparallel double-grating structure in a spectral-beam combining technique, where two gratings are placed nonparallel satisfying the Littrow mount in the focal region of the convergent lens. The most attractive advantage of this approach is that it will compress the spectral span into half of its original spectrum, which means the number of combined elements can be doubled in the gain range of diode lasers. Experimental results demonstrate that the CW output power of the combined beam is 30.9 W with a spectral span of 7.0 nm, compared with its original spectrum span of 13.6 nm, and the spectral beam combining efficiency is 70.5%. In consideration that a single grating could have a high efficiency of >97% in a bandwidth of over ten nanometers, the efficiency loss of the grating pair should be less than 6%, which is acceptable for most applications, so this method of using double gratings should be highly interesting for practical applications when a nearly doubled number of diode lasers could be combined into one single laser compared with the previous single-grating methods.
A high pulse repetition frequency (PRF), high energy Ho:YAG laser directly pumped by a Tm-doped fiber laser and its application to a mid-infrared ZnGeP2 (ZGP) optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is demonstrated. The maximum polarized 2.09 μm laser pulse energy is 13.46 mJ at a PRF of 1 kHz. The corresponding peak power reaches 504 kW. In a double-resonant ZGP-OPO, a maximum mid-infrared laser pulse energy of 1.25 mJ, corresponding to a peak power of 79 kW, is accomplished at a PRF of 3 kHz. The nonlinear conversion efficiency reaches 41.7%. The nonlinear slope efficiency reaches 53.3%.
We experimentally compare the output abilities of lightly and heavily doped Ti:Sapphire (Ti:S) amplifiers with diameters as large as 150 mm. Although a lightly doped Ti:S is more favorable to overcome parasitic lasing (PL) and transverse amplified spontaneous emission (TASE), the self-phase-modulation (SPM) effect becomes more pronounced when a longer crystal is used. Recompression of the amplified, stretched pulses can be seriously affected by the SPM effect. We then propose a temporal multi-pulse pump scheme to suppress PL and TASE in a thin, heavily doped Ti:S crystal. This novel temporal multi-pulse pump technique can find potential applications in 10 PW chirped-pulse amplification laser systems.
Broad-area diode lasers usually supply high output power but low lateral beam quality. In this Letter, an on-chip combined angled cavity is proposed to realize narrow lateral far field patterns and high brightness. The influence of included angles, emitting facets on output power, and beam quality are investigated. It demonstrates that this V-junction laser is able to achieve a single-lobe far field at optimal cavity length with a 3.4 times improvement in brightness compared with Fabry–Perot (F-P) cavity lasers. The excited high-order modes at a high injection level reduce the brightness, but it is still 107% higher than that of F-P lasers.
The cavity transmission spectrum is experimentally investigated in Λ-type three-level atoms coupled to a standing-wave cavity system. It is shown that the dark-state polariton peak is not generated at resonance but rather at off-resonance. The theoretical analysis reveals that the absence of an on-resonance dark-state polariton peak is mainly caused by the strong absorption of the intracavity medium to the probe cavity mode counterpropagating with the coupling field due to the Doppler shift in the hot atoms. Moreover, the optimal frequency position of the cavity mode for an efficient dark-state polariton peak is also demonstrated.
We experimentally demonstrate a cascaded Raman scattering continuum, utilizing a compact mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser based on a nonlinear polarization rotation technique in the all normal dispersion regime. There is no physical filter or polarization controller in the oscillator, and a different mode-locked operation is achieved, corresponding to the extra fiber location in the oscillator. The broadband spectrum generation owes to the enhanced stimulated Raman scattering progress. The maximum output average power and peak power are 14.75 nJ and 18.0 W, and the short coherence light is suited for optical coherence tomography.
We report a 307 W 1018 nm Yb-doped fiber laser pumped by a single 976 nm laser diode. The cavity slope efficiency is up to 75.9% and the amplified spontaneous emission is suppressed by 54 dB. The beam quality of the output laser has an M2 factor of 1.17. Effective thermal management is considered to ensure the stable operation of our system. The power stability at the maximum output power level is measured during a period of 0.5 h and the power fluctuation is less than 0.8%. This architecture can be an effective high brightness pump source of core-pumping high-power fiber amplifiers.
The laser performance of a new Yb:germanophosphate (Yb:GP) glass is investigated. A maximum output power of 826 mW at 1063 nm is achieved with direct diode pumping at 976 nm. The wavelength is tuned from 1034.47 to 1070.83 nm, corresponding to a tuning range of 36.36 nm. Thermal lens effects are investigated to optimize the optical cavity.
We demonstrate the generation of mode-locked pulses in an erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) by using a new manganese-doped cadmium selenide quantum-dots-based saturable absorber. The laser produces a soliton pulse train operating at 1561.1 nm with a repetition rate of 1 MHz, as the pump power is varied from 113 to 250 mW. At the maximum pump power, we obtain the pulse duration of 459 ns with a signal-to-noise ratio of 50 dB.
Far-field blooming, a serious far-field dependence on driving current, affects the stability of beam quality and applications of broad-area (BA) diode lasers. In this Letter, the lateral ridge waveguide (LRW) is introduced to BA lasers by a simple and cost-effective approach to control the far-field stability and beam divergence. The influences of LRW length on output power, near- and far-field, are investigated and it is found that the optimized LRW length is able to improve both the far-field blooming and output power. The mechanism behind this is analyzed and a 0.13°/A dependence of lateral divergence angle on the injection current is achieved.
A fused silica glass micro-channel can be formed by chemical etching after femtosecond laser irradiation, and the successful etching probability is only 48%. In order to improve the micro-channel fabrication success probability, the method of processing a high-temperature lattice by a femtosecond laser pulse train is provided. With the same pulse energy and scanning speed, the success probability can be increased to 98% by optimizing pulse delay. The enhancement is mainly caused by the nanostructure, which changes from a periodic slabs structure to some intensive and loose pore structures. In this Letter, the optimum pulse energy distribution ratio to the etching is also investigated.
Accurate and precise wavelength controlling of narrowband excimer lasers is essential for the lithography of an integrated circuit. High-precision wavelength tuning and calibration of a line-narrowed ArF laser are presented in this work. The laser spectrum is narrowed to a sub-picometer with a line narrowing system. Absolute wavelength calibration of the line-narrowed laser is performed based on the optogalvanic (OG) effect using iron hollow cathode discharge (HCD). An sccuracy of better than 0.1 pm for wavelength tuning and calibration is achieved with our homemade wavemeter.
We demonstrate a continuous-wave (CW) dual-wavelength Nd:YVO4 laser working at 1064 and 1066 nm simultaneously. The method of Nd:YVO4 crystal angle tuning is used to balance the ratio of the stimulated emission cross sections of the two wavelengths, leading to the realization of a simultaneous dual-wavelength operation from only one laser. The experimental results show that at a 2.85 W pump power, the maximum output powers at wavelengths of 1064 and 1066 nm are 0.55 and 0.54 W, respectively. The linear resonate cavity is as short as 10 mm, which gives the laser the advantages of a miniature configuration and low threshold. Such a dual-wavelength laser can be very attractive for the development of compact THz sources based on difference frequency generation.
We propose and demonstrate a novel single fiber optical tweezer based on a graded-index multimode fiber (GIMMF), which works with a free length GIMMF (>30 cm). We achieve a three-dimensional stable trap of yeast cells by using the GIMMF optical tweezers. Compared with the single-mode fiber optical tweezers, the GIMMF optical tweezers possess large optical trapping forces. Owing to the freedom of the GIMMF length, the fabrication of the GIMMF optical tweezers is simple, repeatable, and highly efficient. The GIMMF tweezers have the penitential to become a new member of the single fiber optical tweezers family and have a wide range of applications in the medical and biological cytology fields.
We research some properties of parasitic lasing (PL) in the Ti:sapphire chirped pulse amplifier with the crystal diameter of 100 mm. The evolutionary process from the spontaneous emission to the PL and its influence on amplified output energy, spectrum, and beam profile are experimentally measured. The threshold of PL in the crystal is 22 J, and the output signal can still keep rising with the pump when the pump energy is below 38 J. The PL has no obvious impact on the output spectrum and beam profile besides the energy.
An elliptical initial polarization state is essential for generating mode-locked pulses using the nonlinear polarization rotation technique. In this work, the relationship between the ellipticity ranges capable of maintaining mode-locked operation against different pump power levels is investigated. An increasing pump power, in conjunction with minor adjustments to the polarization controller’s quarter waveplate, results in a wider ellipticity range that can accommodate mode-locked operation. Other parameters such as noise, pulsewidth, and average output power are also observed to vary as the ellipticity changes.
We experimentally demonstrate that optical tweezers can be used to accelerate the self-assembly of colloidal particles at a water–air interface in this Letter. The thermal flow induced by optical tweezers dominates the growth acceleration at the interface. Furthermore, optical tweezers are used to create a local growth peak at the growing front, which is used to study the preferential incorporation positions of incoming particles. The results show that the particles surfed with a strong Marangoni flow tend to fill the gap and smoothen the steep peaks. When the peak is smooth, the incoming particles incorporate the crystal homogeneously at the growing front.
Employing 0.3 nm diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as saturable absorbers, we demonstrate a passively mode-locked fiber laser operating at 1950 nm. The 0.3 nm diameter SWCNTs are prepared by pyrolyzing dipropylamine in the channels of zeolite crystals MgAPO-11 (AEL). The laser pumped by a 1550 nm laser source produces 972 fs pulses with a spectral width at half-maximum of 4.2 nm and a repetition rate of 21.05 MHz, an average output power of 2.3 mW corresponding to the maximum pump power of 420 mW with a 10% output coupler.
A high power continuous-wave single-frequency green fiber laser by second-harmonic generation of a Yb-doped fiber amplifier (YDFA) is developed. A linearly polarized single-mode fiber amplifier produces a 60 W infrared laser at 1064 nm with a 103 W incident diode pump laser at 976 nm, corresponding to an optical conversion efficiency of 58%. An external bow-tie enhancement cavity incorporating a noncritically phase-matched lithium triborate crystal is employed for second-harmonic generation. A 33.2 W laser at 532 nm is obtained with a 45 W incident 1064 nm fundamental laser, corresponding to a conversion efficiency of 74%.
A mode-locked (ML) picosecond ytterbium-doped thin disk laser using a monolayer MoS2 as the saturable absorber (SA) is demonstrated. The monolayer MoS2 is fabricated through the method of low-pressure chemical vapor deposition. The laser directly produces stable ML picosecond pulses at a slope efficiency of 9.71%. The maximum output power is approximately 890 mW, while the corresponding repetition, pulse energy, and pulse duration are 48.6 MHz, 18.3 nJ, and 13.1 ps, respectively. Results suggest that the monolayer MoS2 is a promising SA for ultrafast lasers system.
We demonstrate a single-longitudinal-mode Ho3+:YVO4 unidirectional ring laser based on the acousto-optic effect, utilizing the features of the acousto-optical Q switch and half-wave plate to achieve unidirectional operation. The maximum power achieved in the single-longitudinal-mode at 2053.9 nm is 941 mW when the absorbed power is set as 4.4 W, yielding a nearly 50% slope efficiency. The M2 factor is 1.1. The results show that such a technique offers a potentially promising new method for achieving a high power and narrow linewidth 2 μm single-longitudinal-mode laser.
A frequency-stabilized laser system at 1572 nm for space-borne carbon dioxide (CO2) detection LIDAR to realize the precise measurement of the global atmospheric CO2 concentration is presented in this Letter. A distributed-feedback laser diode serves as the master laser (ML) and is wavelength locked to the CO2 line center at 1572.0179 nm using the external frequency modulation technique. The root mean square frequency drift is suppressed to about 50 kHz at an average time of 0.1 s over 8 h. Based on optical phase-locked loops, an online seeder and an offline seeder are offset locked to the reference laser at 1572.024 and 1572.081 nm, respectively, retaining virtually the same frequency stability as the ML.
A constant elastic alloy is a widely used material with a high elastic modulus and an excellent wave velocity consistency. Different morphologies on the constant elastic alloy surface are observed through femtosecond laser irradiation. When the laser average fluence is set to 0.58 J/cm2 and 200 laser pulses, with the increasing depth of distilled water, the period of the laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) becomes shorter accordingly. The higher the ethanol concentration is, the more spot-shaped structures will be formed among the surface structures when the depth of the coverage of ethanol is 2 mm. The period of the LIPSS reaches its maximum when the concentration of ethanol is 80%.
A burst of six pulses with an average power of 38.7 W are obtained for a pulse-burst picosecond 1064 nm laser system at 1 kHz. The six pulses have equal amplitudes and pulse spacings of 800 ps, the beam quality of the M2 factor is less than 2, and the pulse width is 67 ps. Seed pulses are broadened from 22 to 136 ps by single-pass volume Bragg gratings. A laser-diode end-pump Nd:YVO4 beam-splitting amplifier is used to divide and amplify a single pulse into six pulses. An Nd:YAG regenerative amplifier and a single-pass high-gain amplifier are applied.
A scheme for measuring the intra-cavity round-trip loss of an all-solid-state single-frequency laser by inserting a type-I noncritical phase-matching nonlinear crystal introducing nonlinear loss into the resonator is presented. The intra-cavity round-trip loss is theoretically deduced by analyzing the dependence of the fundamental-wave (FW) and second-harmonic-wave (SHW) powers on the pump factor and the nonlinear conversion factor of the single-frequency laser and experimentally measuring them by recording different FW and SHW powers, which are decided by the temperature of the nonlinear crystal. The measured intra-cavity round-trip loss and pump factor are 4.84% and 6.91% W 1, respectively. The standard deviations of the measured intra-cavity round-trip loss and the pump factor are 0.26% and 0.07%, respectively. This scheme is very suitable for measuring the intra-cavity round-trip loss of a high-gain solid-state single-frequency laser.
The propagation of a filamentary laser beam at an air-glass surface is studied by setting the incident angle satisfying the total reflection condition. The images of the trajectory of the filamentary laser beam inside the sample and the output far-field spatial profiles are measured with varying incident laser pulse energies. Different from the general total reflection, a transmitted laser beam is detected along the propagation direction of the incident laser beam. The energy ratio of the transmitted laser beam depends on the pulse energies of the incident laser beam. The background energy reservoir surrounding the filament core can break the law of total reflection at the air-glass surface, resulting in the regeneration of the transmitted laser beam.
We experimentally demonstrate the generation of sub-100-fs pulses from a diode-pumped passively mode-locked Yb:Y3ScAl4O12 (Yb:YSAG) ceramic laser. Stable mode-locked pulses as short as 96 fs at the central wavelength of 1052 nm with a repetition rate of ~102 MHz are obtained. The laser has a maximum average output power of 51 mW. To the best of our knowledge, these are so far the shortest pulses and the first demonstration of sub-100-fs pulses obtained from the mode-locked Yb:YSAG ceramic lasers.
The pulse characteristics of a laser diode dual-end-pumped electro-optic Q-switched Nd:LuAG ceramic laser at various repetition rates are presented. The largest output pulse energy of 11 mJ is realized at the repetition rate of 100 Hz with pump energy of 84.3 mJ, and the slope efficiency in respect to pump pulse energy is 18.6%. The single pulse peak power reaches up to 1.57 MW. Using Nd:LuAG ceramic as the amplification medium seeded by an Nd:YAG laser of 5.2 mJ, a 10.3 mJ amplified pulse is obtained with pump pulse energy of 42.8 mJ, corresponding to an extraction efficiency of 11.9%.
We experimentally demonstrate a Faraday laser at Rb 1529 nm transition by using a performance-improved Rb electrodeless-discharge-lamp-based excited-state Faraday anomalous dispersion optical filter as the frequency-selective element. Neither the electrical locking scheme nor the additional frequency-stabilized pump laser are used. The frequency of the external-cavity diode laser is stabilized to the Rb 1529 nm transition, and the Allan deviation of the Faraday laser is measured by converting the optical intensity into frequency. The Faraday laser can be used as a frequency standard in the telecom C band for further research on metrology, microwave photonics, and optical communication systems.
We report a continuous-wave Er:ZBLAN fiber laser with the operation wavelength reaching 3.68 μm. The mid-infrared Er:ZBLAN fiber laser is pumped with the dual-wavelength sources consisting of a commercial laser diode at 970 nm and a homemade Tm-doped fiber laser at 1973 nm. By increasing the launched pump power at 1973 nm, the laser wavelength can be switched from 3.52 to 3.68 μm. The maximum output power of 0.85 W is obtained with a slope efficiency of 25.14% with respect to the 1973 nm pump power. In the experiment, the laser emission at 3.68 μm is obtained with a significant power of 0.62 W, which is the longest emission wavelength in free-running Er:ZBLAN fiber lasers.
Sodium-ethane excimer pairs are studied and proved to be a great choice of excimer pumped sodium laser (XPNaL) gain media. The lifetime of the sodium D2 line is studied in a sodium-ethane excimer system excited by a 553 nm laser, and the observed phenomenon of lifetime lengthening is discussed. Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) of the sodium D2 line is successfully obtained, and its time-resolved and spectroscopic characteristics are studied experimentally. According to the intensity of the ASE signal under different sodium vapor atom densities, the sodium D2 line gain feature of sodium-ethane excimer pairs excited by the 553 nm laser is concluded.
We demonstrate the electrical beat note analysis and radio frequency (RF) injection locking of a continuous wave (cw) terahertz quantum cascade laser (QCL) emitting around 3 THz (~100 μm). In free running the beat note frequency of the QCL shows a shift of ~180 MHz with increasing drive current. The beat note, modulation response, injection pulling, and terahertz emission spectral characteristics in the different current regimes I, II, and III are investigated. The results show that in the current regime I close to the laser threshold we obtain a narrower beat note and flat response to the RF modulation at the cavity round trip frequency. The pulling effect and spectral modulation measurements verify that in the current regime I the RF injection locking is more efficient and a robust tool to modulate the mode number and mode frequency of terahertz QCLs.
A dual-wavelength fiber laser operating at the 1550 nm region using a side-polished arc-shaped fiber with deposited ZnO nanoparticles is proposed and demonstrated. The arc-polished fiber is fabricated by using a simple but novel approach in which a silicon carbide paper polishes one side of a conventional single-mode fiber. An arc-polished fiber with a length of 2.25 mm and an insertion loss of 0.95 dB is obtained and deposited with ZnO nanoparticles by the drop-cast method. A stable dual-wavelength output is obtained at 1562.5 and 1563.4 nm at peak powers of 9.3 and 10.1 dBm, respectively, as well as a signal-to-noise ratio of 28.4 dB and a channel spacing of 0.9 nm. Both lasing wavelengths also have narrow linewidths of between 0.045 and 0.049 nm and show little to no wavelength or power fluctuations over continued testing.
A novel black phosphorus (BP) solution saturable absorber (SA) is fabricated by the liquid-phase-exfoliated method and successfully used for passively Q-switched (QS) Nd:YVO4 laser. Compared with a traditional solid SA, a BP solution SA possesses more excellent optical transparency and higher damage resistance. The shortest pulse duration and highest average output power are measured to be 119 ns and 1.23 W, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, both of them are the best results among QS solid-state lasers with BP-based absorbers so far. The repetition rate is in the range of 533.2 to 722 kHz. The results indicate the potential application of the BP solution SA into high-power solid-state pulse lasers.
We present a lamp-pumped Nd: phosphate glass laser amplifier delivering up to 1 J of pulse energy at 1053 nm with a repetition rate of 1 Hz and an injected pulse energy of 2.5 mJ. The amplifier system employs a beam-shaping module and a four-pass, lamp-pumped amplifier. The thermally induced wavefront distortion is mitigated and a uniform gain distribution is obtained by a four-lamp-pumped laser head in the amplifier. Thus, an excellent beam quality is obtained.
We report a simple and compact all-fiber laser system that is capable of generating widely tunable femtosecond pulses from 1.6 to 2.32 μm. The pulses are produced by utilizing the soliton self-frequency shift in a highly nonlinear fiber pumped by an Er-doped mode-locked fiber laser. Two stages of single-clad Tm:fiber amplifiers are used to amplify the pulses to a higher pulse energy of 10.9 nJ with pulse width of 94 fs, and corresponding to peak power of 105 kW at around 1.93 μm. Running a few hours, the all-fiber laser system exhibits exceptional stability with a signal-to-noise ratio as high as 70 dB.
An external-cavity semiconductor laser with nonlinear optical feedback to generate broadband chaos with time delay signature (TDS) suppression is investigated. The system is composed of three semiconductor lasers, one of which is regarded as the chaos generator, while the other two play a role of a built-in nonlinear modulator in the external cavity of the generator. The results show that by properly setting the feedback strength and time delay of the first semiconductor laser in the nonlinear modulator, the TDS embedded in the intensity and phase time-series of the chaos can be effectively concealed in a wide range of frequency detuning.
In this work a passively Q-switched dual-wavelength ytterbium-doped fiber laser using a titanium dioxide-based saturable absorber is proposed and proven. The system also utilizes a side-polished fiber in a ring cavity configuration to obtain the desired pulse train. A stable dual-wavelength pulse output is obtained at 1034.7 and 1039.0 nm, with a maximum pulse energy of 2.0 nJ, and a shortest pulse width of 3.2 μs. The generated pulse train is stable, and has a pulse repetition rate from 31.2 to 64.5 kHz.
We present a hybrid adaptive optics system for a kW-class solid-state slab master oscillator power amplifier laser that consists of both a low-order aberration corrector and a 59-actuator deformable mirror. In this system large defocus and astigmatism of the beam are first corrected by the low-order aberration corrector and then the remaining components are compensated by the deformable mirror. With this sequential procedure it is practical to correct the phase distortions of the beam (peak to valley up to 100 μm) and the beam quality β is successfully improved to 1.9 at full power.
We report a cladding-pumped actively Q-switched ring Tm-doped fiber laser (TDFL). This laser is Q-switched by a free space acousto-optic modulator. A pulse energy up to 150 μJ with a pulse width of 207 ns at a repetition rate of 100 Hz is achieved for a cavity optical length of 6.68 m. The pulse amplitude’s stability at this repetition rate is better than 95%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first free space structure Q-switched ring TDFL report.
We demonstrate the generation of Q-switched pulses from an ytterbium-doped fiber laser (YDFL) using quantum dot (QD) CdSe as a passive saturable absorber (SA). The CdSe QD is fabricated by the synthesis of CdO, Se, and manganese acetate and paraffin oil and oleic acid as the solvent and surfactant, respectively. The CdSe QD is then doped into poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA) via an emulsion polymerization process. A PMMA-hosted CdSe QD thin flake with a homogeneous end surface is then formed and placed between two ferrules and assembled in a YDFL cavity to achieve the Q-switching operation with a repetition rate of 24.45 to 40.50 kHz while varying the pump power from 975 to 1196 mW. The pulse width changes from 6.78 to 3.65 μs with a maximum calculated pulse energy at 0.77 μJ at a pump power of 1101 mW. This work may be the first demonstration of CdSe QD-based Q-switching in an all-fiber configuration that should give proportional insight into semiconductor QD materials in photonics applications.
Tadpole-shaped Au nano-particles with controllable tails are successfully fabricated by simply using laser fragmentation of separated Au nano-spheres in liquid. The optimum laser power densities (1.5–3 GW/cm2) can enable part of the individual Au nano-sphere to be re-melted, released, and ultra-rapidly recondensed/crystallized on the outside of the original region. We find that the length of the tail in a tadpole-shaped Au nano-particle significantly increases from about 10 to 25 nm by increasing the laser power density. Benefiting from the unique structural features, the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) absorption spectra of the tadpole-shaped Au nano-particles become broader by increasing the tail length. Moreover, the LSPR absorption band also exhibits a noticeable red shift from about 520 to 650 nm. Our results provide a convenient and valuable strategy to fabricated novel anisotropic-shaped nano-structures with fascinating properties.
Incipient plasmonic bubble formation is observed around gold nanopillars with different inter-nanopillar separations. The experimental measurements and theoretical analysis show that the nanobubble formation is due to the enhanced plasmonic resonance rather than from the laser heating. Inter-nanopillar distribution may lead to threshold fluence variations. The lifetime of plasmonic bubbles can reach several minutes. Furthermore, both the radius and the growth rate of the plasmonic nanobubble increase as the inter-nanopillar distribution decreases. Smaller-spacing distributed arrays produced larger bubbles. The maximum growth rate of the bubbles can be reached at about 883.5×10 6 m/s on 1 μm nanopillars, but it is only 56.9×10 6 m/s on 4 μm nanopillars.
We report on the amplification of high-average-power and high-efficiency picosecond pulses in a self-made very-large-mode-area Yb-doped photonic crystal fiber (PCF). The PCF with a core diameter of 105 μm and a core numerical aperture of 0.05 is prepared by the sol-gel method combined with the powder sintering technique. The fiber amplification system produces the highest average power of 255 W at a 10 MHz repetition rate with a 21 ps pulse duration corresponding to a peak power of 1.2 MW. This result exemplifies the high-average-power and high-peak-power potential of this specifically designed fiber.
In this Letter, a single-frequency fiber laser using a molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) thin film as a saturable absorber is demonstrated. We use a short length of highly Yb-doped fiber as the gain medium and a fiber ferrule with MoS2 film adhered to it by index matching gel (IMG) that acts as the saturable absorber. The saturable absorber can be used to discriminate and select the single longitudinal modes. The maximum output power of the single-frequency fiber laser is 15.3 mW at a pump power of 130 mW and the slope efficiency is 15.3%. The optical signal-to-noise ratio and the laser linewidths are ~60 dB and 5.89 kHz, respectively.
We demonstrate a scheme to use a Littman configuration external cavity diode laser (ECDL) as a stable-frequency light source to stabilize two cw single-mode Ti:sapphire lasers for laser cooling of magnesium fluoride molecules. An ECDL based on the Littman configuration is constructed and stabilized by a digital signal processor system. We stabilize the frequency of our ECDL to ±0.77 MHz precision over 10 h and the Allan standard deviation reaches 2.6×10 11 at an integration time of 10 s. We lock two Ti:sapphire lasers through a transfer cavity, and either laser has a long-term frequency stability of ±2.5 MHz.
Two types of acousto-optically Q-switched Nd:YVO4/KTA singly resonated optical parametric oscillators are performed. One is signal resonant, where a 1.5 μm wave resonates while a 3.5 μm wave does not. The other is idler resonant, where a 3.5 μm wave resonates while a 1.5 μm wave does not. All the experimental elements are kept the same for these two schemes except for the coatings of the optical parametic oscillator cavity output coupler. For these two kinds of lasers, the output characteristics of the threshold, output power, pulse width, peak power, and beam quality are measured and compared.
Based on the modified ramp and fire technique, a novel injection seeding approach with real-time resonance tracking is successfully demonstrated in a single-frequency Nd:YAG pulsed laser. Appling a high-frequency sinusoidal modulation voltage to one piezo actuator and an adjustable DC voltage to another piezo actuator for active feedback, single-mode laser output with high-frequency stability is obtained, and the effect of the piezo hysteresis on the frequency stability can be eliminated for a laser diode pumped Q-switched Nd:YAG laser at a repetition rate of 400 Hz.
We demonstrate a diode-pump Tm3+-doped all-fiber laser operating at 1908 nm based on a master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) configuration. In our work, 152 W of laser output power is generated by a total incident pump power of 434 W at 790 nm, corresponding to the total optical efficiency of 35%. The laser wavelength is 1908.29 nm. To the best of our knowledge, it is the highest output power reached around 1908 nm with such a narrow linewidth of 0.18 nm based on a MOPA configuration.
Measurements of the excitation power-dependence and temperature-dependence photoluminescence (PL) are performed to investigate the emission mechanisms of InGaN/GaN quantum wells (QWs) in laser diode structures. The PL spectral peak is blueshifted with increasing temperature over a certain temperature range. It is found that the blueshift range was larger when the PL excitation power is smaller. This particular behavior indicates that carriers are thermally activated from localized states and partially screen the piezoelectric field present in the QWs. The small blueshift range corresponds to a weak quantum-confined Stark effect (QCSE) and a relatively high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) of the QWs.
We report a monolithic Tm:YLF micro laser in this Letter. In order to improve the relaxation oscillation of the laser, both ends of the crystal are coated, making the Tm:YLF crystal itself a resonant cavity. The micro laser is pumped by a 792 nm laser diode operated in the continuous wave (CW) mode. We obtain maximum output powers of 7.78 and 10.4 W at the total incident power of 43.6 W with focus lenses of 37.5 and 40 mm, respectively, corresponding to the slope efficiencies of 25.6% and 40.0% and the optical–optical conversion efficiencies of 17.8% and 23.8%. It is clear that the amplitude of the relaxation oscillation is smaller and the beam quality is better with the focus length of 37.5 mm; however, the laser with the focus length of 40 mm produces a higher output power and a more stable wavelength centering at 1878.44 nm.
We present a diode-pumped high-energy ceramic Nd:YAG planar waveguide that is demonstrated as a record in output energy for the ceramic planar waveguide fabricated by nonaqueous tape casting and solid-state reactive sintering. Under a repetition rate of 100 Hz and a pulse width of 250 μs, a maximum output pulse energy of 327 mJ is obtained with a beam quality factor of =2.6×7.0. The corresponding peak power is 1308 W. The extraction efficiency of the system is about 56%.
We present a compact, low-noise, and inexpensive optical phase-lock loop (OPLL) system to synchronize the frequency and the phase between two external cavity diode lasers. Based on a direct digital synthesizer technique, a programmable radio-frequency generator is implemented as the reference signal source. The OPLL has a narrow beat note linewidth below 1 Hz and a residual mean-square phase error of 0.06 rad2 in a 10 MHz integration bandwidth. The experimental test results prove the competent performance of the system, which is promising as a low-budget choice in atomic physics applications.
We investigate the dynamic processes of the Nd:YAG pulse laser ablation of fused silica by ultrafast time-resolved optical diagnosis with a nanosecond time resolution. The evolution process of plasma expansion in air and shock waves propagation in the bulk are both obtained with spatial and temporal resolutions. Laser-induced damage in the bulk of fused silica with filaments and shock waves are observed. Thermoelastic wave, mechanical wave, and shock wave dependence on the laser fluence and intensity of the plasma are analyzed. The shock pressure P and temperature T calculated through the measured shock velocity D and the Hugoniot data of fused silica are measured.
Metal hydrazone complex thin films are used as laser patterning materials, and the patterns with a minimum resolution of about 78 nm are successfully obtained by the laser writing setup (λ=405 nm, NA=0.9). The minimum resolution is only about 1/8 of the writing spot size. In the formation of patterns, there is only a single step for forming patterns by the laser heating-induced clear thermal gasification threshold effect without any other development processes such as wet etching. This work provides an effective method for directly achieving nanoscale-resolved pattern structures with diode-based maskless laser writing lithography at visible light wavelengths.
We demonstrate an efficiency-enhanced picosecond (ps) mid-infrared radiation via optical parametric downconversion. Based on a cascaded periodically poled MgO-doped stoichiometric lithium tantalate crystal (MgO:sPPLT), a tandem optical parametric oscillation-optical parametric amplification (OPO-OPA) process is achieved. Compared with a single OPO process, the conversion efficiency obtains an enhancement of 71%.
In this Letter, a simple and passively mode-locking Yb-doped all fiber laser using a nonlinear polarization rotation technique operating under dissipative soliton (DS) or dissipative soliton resonance (DSR) conditions is proposed. Furthermore, using a combination of a bandpass filter and a Loyt filter, tunable single-wavelength or dual-wavelength operation under two different conditions is realized, respectively. The tunable single-wavelength DS laser has a 5 nm tuning range from 1029 to 1034 nm with a pulse width of 110 ps. The tunable single-wavelength DSR operation laser has a range of 4 nm. In-depth research on the mechanism of the conversion between DS and DSR is carried out. Particularly, under dual-wavelength DSR operation, the obtained step-like pulses consist of two rectangular pulses with different energies. This work could help give a deeper insight into normal dispersion pulses.
An improved model-based wavefront sensorless adaptive optics algorithm is proposed for laser beam cleanup. Deformable mirror (DM) eigenmodes are used to replace traditional Lukosz modes in order to avoid DM fitting errors. The traditional method is based on a sophisticated calibration process and solving linear equations. In our method, coefficients of DM eigenmodes are estimated by adding bidirectional modal biases into the system and then solving parabolic equations. The calibration process is omitted in our method, which makes it more feasible. From simulation and experimental results, the corrective accuracy of the improved method is higher than the traditional one.
Diffractive optics is an important technique for beam shaping with high light efficiency and strong diffraction pattern flexibility. Since the diffraction angle is limited by the unit size of the diffractive optical element (DOE), the size of the required diffraction pattern is always rather small. In this Letter, refractive/diffractive hybrid optical elements (RDHOEs) consisting of a DOE and a lens are used to realize beam shaping for a large diffraction pattern. The lens, as the component of the RDHOEs, can not only be concave but also convex, and the double sampling Fresnel diffraction algorithm is developed for the design of these two types of RDHOEs. The simulation and experimental results provide solid evidence to demonstrate the proposed method with the pure phase spatial light modulator.
The stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) threshold affected by repetition rate and pulse duration in a single-frequency nanosecond pulsed fiber amplifier is studied. The experimental results demonstrate that the SBS threshold can be improved either by reducing the repetition rate or by narrowing the pulse duration; however, the average power may be limited in some cases. Otherwise, two evaluation methods for the SBS threshold in the fiber amplifier are compared and discussed, aiming to obtain a more accurate description for the SBS threshold in our single-frequency amplifier system.
Hybrid octagonal-ring microlasers are investigated for realizing a stable output from a silicon waveguide based on a two-dimensional simulation. The inner radius of the ring is optimized to achieve single-mode and low-threshold operation. Using the divinylsiloxane-benzocyclobutene (DVS-BCB) bonding technique, a hybrid AlGaInAs/Si octagonal-ring microlaser vertically coupled to a silicon waveguide is fabricated with a side length of 21.6 μm and an inner radius of 15 μm. A single transverse-mode operation is achieved with a threshold current density of 0.8 kA/cm2 and a side-mode suppression ratio above 30 dB, and a stable output from the lower silicon waveguide is obtained.
We report on the experimental observation of the airflow motion induced by an 800 nm, 1 kHz femtosecond filament in a cloud chamber filled with air and helium. It is found that vortex pairs with opposite rotation directions always form both below and above the filaments. We do not observe that the vortices clearly formed above the filament in air just because of the formation of smaller particles with weaker Mie scattering. Simulations of the airflow motion in helium are conducted by using the laser filament as a heat source, and the simulated pattern of vortices and airflow velocity agree well with the experimental results.
A method for fabricating deep grating structures on a silicon carbide (SiC) surface by a femtosecond laser and chemical-selective etching is developed. Periodic lines corresponding to laser-induced structure change (LISC) are formed by femtosecond laser irradiation, and then the SiC material in the LISC zone is removed by a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid to form grating grooves. Grating grooves with a high-aspect ratio of approximately 25 are obtained. To obtain a small grating period, femtosecond laser exposure through a phase mask was used to fabricate grating structures with a 1.07 μm period on the surface of the SiC.
In this Letter, we demonstrate the anisotropy of laser emission in disordered Nd:ScYSiO5 (Nd:SYSO) crystals cut along the optical indicatrix axes. High-powered lasers with different oscillation wavelengths and polarizations are realized by using different oriented crystals as gain media. For Y-cut crystals, the dual-wavelength laser vibration direction is found to be along the X axis and a maximum output power of 9.43 W is obtained, giving an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 48.8% and a slope efficiency of 51.3%. For X- and Z-cut crystals, 1075 and 1078 nm lasers operating orthogonally polarize oscillate with total output powers of 7.07 and 8.43 W, respectively. The experimental results reveal that the intrinsic anisotropy for the monoclinic disordered laser crystals could make laser design flexible and controllable.
The continuous wave (CW) and passively Q-switched (PQS) performances of diode-pumped Nd:(LaxGd1 x)3Gd5O12 (Nd:LaGGG) at 1.33 μm are achieved for the first time to our knowledge. The maximum CW output power of 5.1 W is obtained with the optical-optical conversion efficiency of 25.3% and the slope efficiency of 26.6%. In the PQS operation, by using the V3+:YAG crystal as the saturable absorber, the maximum average output power, shortest pulse width, largest pulse energy, and highest peak power are measured to be 1.1 W, 27.54 ns, 75.78 μJ, and 2.44 kW, respectively.
We demonstrate wavelength-selectable visible emissions from a miniature crystalline laser that combines the stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) effect in an Nd:YVO4 crystal with intracavity frequency mixing in an angle-tuned beta barium borate (BBO) crystal. The presented laser is operating on demand at any one of three wavelengths in the green-yellow spectral region. Up to 600, 560, and 200 mW output powers at 559, 532, and 588 nm, respectively, are obtained from the continuous wave (CW) laser having a 18 mm long resonator and a 3.8 W laser diode end pumping. The pump threshold for each visible wavelength is less than 0.4 W.
A laser diode array side-pumped Nd:glass square rod amplifier of the dimensions 12 mm×12 mm is designed. The fluorescence is evenly distributed in the Nd:glass amplifier. When the pump power is 66.32 kW, the small signal gain increases by 3.23 times. Under the condition of a 1 Hz repetition frequency, 50 mJ of injected seed-light energy, and a 10 mm×10 mm aperture, the output energy of the laser beam can reach 1.62 J during the four-pass amplification. The output energy stability of the laser pulse is 2.94% (RMS), and the square pulse distortion is smaller than 2. The energy amplification of the injected laser beam from millijoules to joules is realized.
It is demonstrated that high-Q (Q~108) bottle microresonators can be fabricated by using a CO2 laser to heat a vertical single-mode fiber with a small weight attached to its lower end. A tunable continuous-wave laser is used to excite whispering-gallery modes in a bottle microresonator through a fiber taper, and a ringing phenomenon is observed. The observed ringing phenomenon is well explained through the numerical solution of a dynamic equation. In addition, an explicit function is given to describe the light field in the resonator, and the theoretical transmission based on the function also agrees very well with the experimental ringing phenomenon.
Polarization switching (PS) characteristics in a 1550 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) subject to circularly polarized optical injection (CPOI) are experimentally investigated. The results show that, under different biased current, a solitary 1550 nm VCSEL can oscillate at y polarization mode (y mode), two polarization components (PCs) coexistence or x polarization mode (x mode). The PS characteristics induced by CPOI for the VCSEL operating at y mode and x mode are analyzed and the evolutions of dynamical states with the injected power are discussed. Additionally, the mappings of nonlinear dynamical states are given in the parameters space of the injected power and frequency detuning.
A 95 W Nd:YAG laser system pumped by a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) array is described. The laser contains an all-fiber-based seeder, an Nd:YAG regenerative amplifier, and a four-pass amplifier. The laser operates at 300 Hz with energies up to 317 mJ. The beam has a top-hat intensity distribution. The temporal pulse shape is flat in time, and the pulse width can be adjusted in the range of 2–6 ns.
We present a laser frequency locking system based on acousto-optic modulation transfer spectroscopy (AOMTS). Theoretical and experimental investigations are carried out to optimize the locking performance mainly from the view of the modulation frequency and index for the specific scheme of AOMTS. An FWHM linewidth of 63 kHz is achieved and the frequency stability in terms of Allan standard deviation reaches 1.4×10 12 at 30 s. The frequency shifting capacity is validated throughout the acousto-optic modulator bandwidth while the laser is kept locked. This work offers a different but efficient choice for applications calling for both stabilized and tunable laser frequencies.
In order to solve the problem of low measurement accuracy caused by uneven imaging resolutions, we develop a three-dimensional catadioptric vision sensor using 20 to 100 lasers arranged in a circular array called omnidirectional dot maxtric projection (ODMP). Based on the imaging characteristic of the sensor, the ODMP can image the area with a high image resolution. The proposed sensor with ODMP can minimize the loss of the detail information by adjusting the projection density. In evaluating the performance of the sensor, real experiments show the designed sensor has high efficiency and high precision for the measurement of the inner surfaces of pipelines.
A stable passively mode-locked laser of Nd3+:Gd0.5Y2.5Al5O12 (Nd:GYAG) disordered crystal is experimentally investigated both using Z-type and W-type cavities with a semiconductor saturable absorbed mirror. The continuous-wave mode-locked threshold of the absorbed pump power is just 1.8 W. The maximum average output power is 210 mW, which is obtained at the absorbed pump power of 2.3 W. The pulse width is measured to be 11.1 ps assuming a Gaussian shape.
A 1.88 μm Ba(NO3)2-based stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) laser pumped by a potassium-titanyl-phosphate-based optical parametric oscillator (OPO) laser is presented. Under the pumping energy of a 130 mJ 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser, a 40 mJ 1.57 μm laser is achieved; the maximum output energy of the 1.88 μm Raman laser reaches 7.5 mJ with a pulse duration of 5.3 ns at repetition rates of 10 Hz, and the corresponding total optical conversion efficiency is about 5.8%. The combination of the SRS and OPO techniques significantly extends the wavelength from 1.064 to 1.57 μm (OPO) and then demonstrates Stokes-shifting to 1.88 μm (SRS).
Intensive electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) can be generated from interaction of the ultra-intense lasers and solid targets in inertial confinement fusion (ICF), which will detrimentally affect the data acquisition from some electric components. A diagnostic system for EMP measurement inside and outside the ShenGuang-III facility is designed and fabricated in this study. The experimental results indicate that the peak magnitude of EMP reaches up to 3210.7 kV/m and 6.02 T. The received signals depend most on the antenna and target types. The half-hohlraum generates a more intensive EMP radiation than that from the other targets, and the large planar and medium discone capture much stronger signals than the other antennas. In addition, the mechanisms of EMP generation from different targets are discussed. The resulting conclusion are expected to provide the experimental basis for further EMP shielding design.
The length stability of optical cavities is vital in ultra-stable, cavity-stabilized laser systems. Using finite element analysis, we study the length deviation of optical cavities due to thermal expansion and thermo-refractive effects when the incident light power is changed. The simulated fractional length sensitivity of a 7.75-cm-long football cavity to the power fluctuation of incident light is 5×10 14/μW, which is in agreement with the experimental results found by measuring the frequency change of a cavity-stabilized laser when the incident light power is changed. Based on the simulation, the cavity sensitivity to light power fluctuation is found to depend on the cavity size and material.
We report on the continuous-wave (CW) and passive Q-switching performance of a miniature Yb:Y3Ga5O12 crystal laser end pumped by a 935-nm diode laser. A maximum CW output power of 12.03 W is produced with an optical-to-optical efficiency of 54.4%, while the slope efficiency is 63%. In the passively Q-switched operation achieved with a Cr4+:YAG saturable absorber, an average output power of 2.12 W at 1025.2 nm is generated with a slope efficiency of 46% at a pulse repetition rate of 5.0 kHz. The pulse’s energy, duration, and peak power are 424 μJ, 2.3 ns, and 184.3 kW, respectively.
A terahertz excitation source based on a dual-lateral-mode distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser working in the 1.5 μm range is experimentally demonstrated. By optimizing the width of the ridge waveguide, the fundamental and the first-order lateral modes are obtained from the laser. The mode spacing between the two modes is 9.68 nm, corresponding to a beat signal of 1.21 THz. By tuning the bias currents of the phase and DBR sections, the wavelengths of the two modes can be tuned by 2 nm, with a small strength difference (<5 dB) and a large side-mode suppression ratio (SMSR>45 dB).
By investigating the cross-spectral density of partially coherent multi-rotating elliptical Gaussian beams (REGBs) that propagate through a focusing optical system, we obtain the radiation force on a Rayleigh particle. The radiation force distribution is studied under different beam indexes, coherence widths, and elliptical ratios of the partially coherent multi REGBs. The transverse and the longitudinal trapping ranges can increase at the focal plane by increasing the beam index or decreasing the coherence width. The range of the trapped particle radii increases as the elliptical ratio increases. Furthermore, we analyze the trapping stability.
During the formation of sub-wavelength ripples, the initial surface plasmon (SP)-laser interference plays an important role. In this Letter, the effects of grating structures on the distribution of the absorbed laser intensity, SP-laser coupling, free electron distributions, and ablation shapes are investigated by the plasma model, taking into consideration both the laser wave-particle duality and the transient localized changes of material properties. The simulation results show that the grating structures can strongly enhance the energy absorption and SP-laser coupling, which makes the fabrication of sub-wavelength ripples more efficient. It is also found that the ablation shapes, in terms of ablation depths and sub-wavelength ripples periods, are strongly related to the grating structures, which can be used to control micro/nanostructures precisely and uniformly.
We observe a nonlinear response of a dual-wavelength Nd:YAG laser when subjected to low-frequency periodic modulations of cavity losses. The modulation frequency is far from the relaxation oscillation frequency. The harmonic resonances of the two laser wavelengths associated with antiphase intensity oscillations are demonstrated and resonances up to the fourth order were observed. For relatively weak modulation, the intensity oscillation frequency of the laser is equal to the modulation frequency. Harmonic resonances occur under a stronger modulation. We find that more harmonic components appear when the modulation frequency is increased. Furthermore, with enhancing the modulation, the dominant frequency of the intensity oscillations of both wavelengths is shifted toward the higher-order harmonic frequency.
We produce a maximum 1.45 W laser output at 1064 nm using a neodymium-doped silicate glass fiber that has a rectangular core with dimensions of ~6.3 μm×31.5 μm. The measured divergence angles of the output laser in two dimensions are 3.22° and 1.76°, respectively. The output power is stable and limited only by the available pump power.
A wavelength-swept laser is constructed using a free space external cavity configuration coupled with a fiber-based ring cavity at the 850 nm region. The external cavity filter employs a galvo-mirror scanner with a diffraction grating for wavelength selection. The filter is connected to a ring cavity through an optical circulator. The ring cavity contains a broadband semiconductor optical amplifier with a high optical output. The performance of this laser is demonstrated with broad bandwidths and narrow linewidths. The 3 dB linewidth and the bandwidth of this source are 0.05 nm (~20 GHz) and 48 nm, respectively. The maximum output power is 26 mW at 160 mA current.
We report on a spectral beam combination of five narrow-linewidth fiber amplifiers. The five-channel output beams are combined in both the near and far field using a polarization-independent diffraction grating that mainly preserves the beam quality of the individual amplifiers. Each amplifier contains a two-stage preamplifier and a main amplifier delivering about 240 W of optical power, which allows a total combined output power of 1.23 kW with an efficiency of over 95%.
We theoretically investigate the dynamics of thermalization in Au-Ti double-layered film irradiated by a femtosecond laser pulse. A nonequilibrium thermal relaxation model is proposed to study the energy deposition and transport processes during femtosecond laser pulse heating of double-layered film. The maximum phonon temperature on the Au layer can be greatly adjusted by optimizing the thickness of the Au layer. In addition, the effect of Au-layer thickness on the thermalization dynamics of the Au-Ti system is examined in detail. This study provides a new way to increase the resistance of mirrors to thermal damage in applications of high-power lasers.
The temporal evolution of Nd:YAG laser-produced Sn plasma in atmospheric pressures from 5 to 104 Pa is investigated. The results show that the extreme ultraviolet radiation exists only at the beginning of the expansion process for 20 ns. The maximum temperature of 18.7 eV and density of 9.6×1017 cm 3 are measured at 73 ns. The effects of air pressure and laser energy on the process of plasma expansion are investigated. The results indicate that the air pressure has an inhibitory effect on kinetic energy, while the electron density and temperature increase with air pressure.
We propose a novel pulse amplification model to obtain the effective thermal equilibrium time (τETE) for Yb:YAG crystal, where τETE has impacts on the gain recovery and energy extraction. A test amplifier is set up to measure the input fluence, output fluence, and pulse duration. By fitting the numerical values to the experimental data, the effective thermal equilibrium of Yb:YAG crystal at room temperature is found to be between 60 and 120 ps. To our best knowledge, this is the first time that an exact range of effective thermal equilibrium time for Yb:YAG is reported.
We report on the frequency stabilization of Er-doped fiber lasers against rotovibrational absorption lines of molecular H13C14N at 1550 nm by means of the frequency modulation spectroscopy technique. The laser frequency is locked to the saturated dispersion signal of an HCN cell and reached a stability of 0.4×10 11 for a 100 s integration time without frequency modulation.
To obtain a laser output with a high-quality beam and a square, super-Gaussian, flat-top distribution, a high-energy laser needs to conduct spatial reshaping of the geometric outline of an injected Gaussian laser pulse and the non-uniform gain of multi-level energy amplification units. A digital micro-mirror device is very suitable for a working environment that has a high electromagnetic interference in a high-energy laser system. We present an algorithm and an experiment of spatial beam shaping that is based on the use of a digital micro-mirror device. Through secondary shaping, the near-field modulation degree of the beam (the ratio of the maximum value of the light intensity to the average value) decreases from 1.79∶1 (after primary shaping) to 1.24∶1, an improvement of 30.7%. The energy loss is 32.9%. Meanwhile, the beam after secondary shaping possesses extremely strong stability. Under the condition where the input-shaping aperture remains unchanged, the dispersity of the near-field modulation degree of the output beam is only 1.6%. Thus, the influences of the environmental changes and the random distribution of the “noise” in the beam intensity distribution are reduced.
A new shorter T-shaped thermo-stable telescopic resonator is demonstrated in this Letter. By means of thick lens model, a longer 1064-nm telescope linear cavity is designed and simulated first by analyzing the influence of the distance between every two optical elements on the fundamental mode radius on the end mirror and the system stable zone. On the basis of the parameters analyzed, a shorter telescopic composite laser system is presented for both the 1064 and 1319 nm operating lasers that will be applicable to high-quality yellow laser generation by means of sum-frequency technology.
A Collins formula method with a scaling factor between the target and source plane is proposed for laser propagation in optical system design, which can be used to evaluate laser optical system performance and tolerance analysis. The laser propagation in optical systems can be calculated by the Collins integral formula, and an angular spectrum method is derived by coordinate substitution. It is introduced a scaling factor m, making the choice of the observation plane more flexible and the calculation more accurate. A laser optical system is designed, and its tolerance analysis is conducted by the angular spectrum method. The evaluation criterion is the laser spot radius in the far-field, which is defined by 86.5% power in bucket. The radius of the laser spot in 90 m distance is from 0.8 to 1.4 mm by the tolerance analysis, which the ideal expectation is 0.92 mm and the experimental result is 1.01 mm. In the distance of 47 m, the radius is from 0.42 to 0.73 mm by the tolerance analysis, which the ideal expectation is 0.48 mm and the experimental result is 0.46 mm. The experimental results agree with the results of the tolerance analysis well. The focal shift for laser propagation in optical systems is validated. The experimental results confirm the calculation and they prove the use of the method in laser focus optical system design.
We investigate propagation of a finite energy Airy beam in a gradient-index fiber analytically and numerically, and find that the beam not only repeats its intensity features, but also has the phenomenon of self-focusing and self-accelerating periodically. The numerical results show that the beam centroid position and beam width evolve periodically. The radial gradient of the refractive index determines the propagation period for the beam and the truncated parameter affects the amplitude of both the centroid position and beam width.
For polarization switching (PS) and nonlinear dynamic behaviors (NDBs) of an optically injected laser system composed of a master vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) and a slave VCSEL, we put forward a novel manipulation scheme by means of electro-optic (EO) modulation with quasi-phase matched technology. It is found that the PS of the slave VCSEL subject to parallel or orthogonal optical injection takes on a change of periodic oscillation with the applied transverse electric field. The optically injected slave VCSEL can experience different NDBs evolutions when the light from the master laser is modulated by the linear EO effect.
An amplified and narrow-linewidth distributed feedback fiber laser in a master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) configuration is presented. It consists of a distributed feedback fiber laser as the seed laser and an MOPA structure in an all-single-mode fiber system. The optimized narrow-linewidth fiber laser has an over 15% efficient slope. The packaged laser module shows excellent performance including a narrow linewidth of 2 kHz, low relative intensity noise below 100 dB/Hz at the relaxation oscillation frequency, and low phase noise, which make it very suitable for interference and distributed sensing applications.
We report a Q-switched self-Raman third-Stokes laser at a wavelength of 1487 nm, with a YVO4/Nd:YVO4/YVO4 composite crystal and a high-power fiber-coupled diode laser array at 808 nm. The maximal average output power at 1487 nm is measured to be 506 mW, at an incident pump power of 34 W and a pulse repetition frequency (PRF) of 30 kHz. The corresponding optical conversion efficiency is 1.49%. To our knowledge, our Q-switched self-Raman third-Stokes laser at 1487 nm on a YVO4/Nd:YVO4/YVO4 composite crystal is reported for the first time.
Some problems and confusions related to matrix analysis for Gaussian beam reflection are clarified. We can choose right-handed coordinates before and after mirror reflection which is called the traditional coordinate system in this Letter. We can also choose a coordinate system with chirality inversion which is called a novel coordinate system in this Letter. The matrix describing optical components should coincide with the selected coordinate system; errors or confusions will appear otherwise. Spherical mirror reflection and coordinate rotation in nonplanar ring resonators are used to clarify some confusion in previous publications due to disorder of the coordinate system. This work is significant to both Gaussian beam propagation analysis and ring laser resonator design.
We set up a pulsed beam steering system with a simple feedback control method. The system applies an integration circuit to process a 2 μs short pulsed beam with a repetition rate of 25 Hz, and employs an iteration method to correct the beam with a reasonable feedback gain factor. The beam steering system achieves a performance of 30 μm position accuracy and 30 μrad pointing accuracy, and it can not only compensate the drift of the laser source but also correct the external disturbance. The design can be directly applied as a lithography tool.
Nanosecond single- and multiple-pulse laser damage studies on HfO2/SiO2 high-reflection (HR) coatings are performed at 532 nm. For single-pulse irradiation, the damage is attributed to the defects and the electric intensity distribution in the multilayer thin films. When the defect density in the irradiated area is high, delamination is observed. Other than the 1064 nm laser damage, the plasma scalding of the 532 nm laser damage is not pits-centered for normal incidence, and the size of the plasma scalding has no relation to the defect density and position, but increases with the laser fluence. For multiple-pulse irradiations, some damage sites show deeper precursors than those from the single-shot irradiation due to the accumulation effects. The cumulative laser-induced damages behave as pits without the presence of plasma scalding, which is unaffected by the laser fluence and shot numbers. The damage morphologies and depth information both confirm the fatigue effect of a HfO2/SiO2 HR coating under 532 nm laser irradiation.
We report a wavelength swept fiber laser at the 1 μm region based on an actively mode-locked dispersion-tuning technique. The ring-cavity laser uses a 70 cm ytterbium-doped fiber as a gain medium. Mode locking is achieved by the direct modulation of the amplitude modulator, and a ~1000 m single-mode fiber is used to provide the desired intracavity dispersion. By sine-modulating the modulation frequency, a wavelength swept laser with a range of ~30 nm can be achieved at a sweeping rate of 50 Hz. The characteristics of the laser, such as its single-wavelength tuning range, tuning sensitivity, static linewidth and sweeping rate, are also studied experimentally.
Through employing permutation entropy and the self-correlation function, the time-delay signature (TDS) of a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) with variable-polarization filtered optical feedback (VPFOF) is evaluated theoretically. The work shows that the feedback rate η, polarizer angle θp, and filter bandwidth Λ have an obvious influence on the TDS. The evolution maps of the TDS in parameter space (η,Λ) and (η,θp) are simulated for searching the chaos with weak TDS. Furthermore, compared with a VCSEL with polarization-preserved filtered optical feedback and a VCSEL with variable-polarization mirror optical feedback, this VPFOF–VCSEL shows superiority in TDS suppression.
Temporal properties of random lasing under ultrashort pulse excitation are investigated in a two-dimensional disordered medium. The pumping light is described individually and coupled into the rate equations. The Maxwell equations and rate equations are numerically solved by using the finite-difference time domain method. The time evolution of the emission pulse is studied with the variation of the surface-filling fraction, refractive index, and scatterer radius. Results show that the behavior of random lasing depends strongly on the sample parameters. Our work enriches the knowledge about random lasers in the ultrashort pulse pumping regime and offers some guidance for relevant experiments.
We demonstrate a potassium titanyl phosphate-based optical parametric oscillator (OPO) emitting at 1729 nm. A maximum output power of 1.56 W at 1729.4 nm is obtained with an original fundamental laser power of 5.48 W. The pulse with a pulse duration of 11.22 ns exceeds 3 mJ at a 500 Hz repetition rate. To our knowledge this is the highest energy output of an OPO laser emitting around 1.73 μm operating at a 100 Hz order of magnitude. This laser is primarily used for bond-selective imaging of deep tissue, a promising way for diagnosing vulnerable plaques in live patients.
A passively Q-switched mode-locked (QML) Tm:LiLuF4 (LLF) laser with a MoS2 saturable absorber (SA) is demonstrated for the first time, to our best knowledge. For the Q-switching mode, the maximum average output power and Q-switched pulse energy are 583 mW and 41.5 μJ, respectively. When the absorbed power is greater than 7.4 W, the passively QML pulse is formed, corresponding to an 83.3-MHz frequency. The modulation depth in Q-switching envelopes is approximately 50%. Results prove that MoS2 is a promising SA for Q-switched and QML solid-state lasers.
A simple and versatile strategy is designed to successfully fabricate ultrafine TiO2 nano-cages based on the rapid decomposition reaction between amphoteric hydroxide and ammonia solution by pulsed laser ablation of Ti/Al alloy in liquid. With the ammonia concentration (Vammonia:Vwater, where V is volume) increasing from 1∶10 to 1∶4, the diameter and shell thickness of quasi-spherical TiO2 nano-cages substantially decrease from 300 and 60 nm to 9.2 and 2.8 nm, respectively. The obtained results have significant implications for obtaining insight into the properties of the TiO2 porous nano-cages, offering the basis for further fabrication of other nano-cages.
A two-dimensional, transient model is proposed to study the dynamic process of keyhole formation and the material changes during both the laser-on and -off periods. The keyhole shape, temperature field, and velocity field are analyzed. The results indicate that the dynamic changes of the target material in the laser-off period have a great influence on the final structure of the keyhole.
A wireless terahertz (THz) communication link is demonstrated, in which a THz quantum cascade laser and a THz quantum-well photo-detector (QWP) serve as the emitter and receiver, respectively. With the help of the well-matched THz QWP, the optical collection efficiency has greatly been improved. A data signal transmitted over 2.2 m with a low bit error rate (≤1×10 8) and data rate as high as 20 Mbps is achieved, which are almost 1 order of magnitude higher than that previously reported.
We report on the generation of Q-switched and Q-switched mode-locked (QML) pulses in an erbium-doped fiber ring laser by using a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) -based gold nanorod (GNR) saturable absorber (SA). The PVA-based GNR SA has a modulation depth of ~4.8% and a non-saturable loss of ~26.9% at 1.5 μm. A Q-switched pulse train with a repetition rate varying from 18.70 to 39.85 kHz and a QML pulse train with an envelope repetition rate tuning from 20.31 to 31.50 kHz are obtained. Moreover, the lasing wavelengths of the Q-switched pulses can be flexibly tuned by introducing a narrow bandwidth, tunable filter into the laser cavity. The results demonstrate that the GNRs exhibit good optical performance and can find a wide range of applications in the field of laser technology.
We propose an adaptive parallel coordinate (APC) algorithm for quickly forming a series of focused spots at a multimode fiber (MMF) output by controlling the MMF input field with a spatial light modulator (SLM). Only passing over the SLM once, we can obtain SLM reflectance to form focused spots on different positions. Compared with the transmission matrix method, our APC does not require iterations and massive calculations. The APC does not require as much access device time as the adaptive sequential coordinate ascent (SCA) algorithm. The experiment results demonstrate that the time taken to form 100 spots with our APC is 1/54th the time with the SCA.
We demonstrate a narrow-linewidth linearly polarized 1645 nm Er:YAG laser, directly diode-pumped by a fiber-coupled continuous-wave laser diode at 1532 nm. Passive Q-switching is realized by a few-layer graphene saturable absorber. A maximum polarized average output power of 3.13 W is achieved at 23.28 W incident pump power. A pulse energy of as much as 58.8 μJ and pulse width of 4.21 μs are yielded at a 53.2 kHz pulse repetition rate. The spectrum and linewidth of the output beams are measured to be 1645.34 and 0.05 nm, respectively. This laser can be useful in the detection of atmosphere pollutants.
The effect of co-doping Y3+ and the doping concentration of Nd3+ on the spectroscopic properties and laser performance of Nd:CaF2 crystals are investigated systematically. For a 0.5% Nd:CaF2 crystal, the emission lifetime at 1.06 μm increases from 18 to 361 μs by co-doping 10 at.% Y3+, while the emission cross section increases to 4.27×10 20 cm2 at 1054 nm. With a 10 at.% doping concentration of Y3+, Nd,Y:CaF2 crystals concentrate emission bands that peak at 1054 nm with shoulders at 1063 nm, and FWHM at about 30 nm. A diode-pumped, highly efficient laser operation is obtained with 0.5% Nd, 10% Y:CaF2 and 0.6% Nd, 10% Y:CaF2 crystals, with slope efficiencies over 30% and 27%, respectively, and a maximum output power up to 901 mW.
A continuous-wave all-solid-state tunable Ti:sapphire laser with compact configuration is presented. The frequency-tuning range extends from 760 to 825 nm by rotating the birefringent filters. When the intracavity etalon is locked on the oscillating frequency of the laser and the length of the resonator is scanned by the piezoelectric ceramics transducer, a maximal continuous frequency-tuning range of 15.3 GHz is realized. The obtained Ti:sapphire laser is successfully applied to scan the saturation absorption spectroscopy of D1 transitions of Rb87 atoms around the wavelength of 794.97 nm.
Self-Q-switching is observed in a bulk Yb:KGd(WO4)2 oscillator without any additional modulating elements. The output power reaches 434.4 mW at a pump power of 13.67 W, corresponding to pulse repetition rate of 125 kHz and a pulse duration of 2.5 μs, respectively. The mechanism of self-pulse formation is explained by the re-absorption effect of the Yb3+ ion in Yb:KGd(WO4)2.
All-fiber signal combiner is a key component for augmenting the fiber laser power. Presently the reported 7×1 signal combiners are all have output fibers with core diameters larger than 100 μm. In order to improve the beam quality of the combiner, a fiber with smaller core of 50 μm diameter is chose to be the output fiber. An all-fiber 7×1 signal combiner is fabricated with measured power transmission efficiency around 99% for each port. The beam quality is improved and the measured M2 are around 6 which are matched well with the theoretically calculated results.
In this Letter, we describe an optical assembly that is designed for the engineering application of the atomic laser cooling techniques. Using a folded optical path scheme, we have built a miniaturized, compact magneto-optical trap (CMOT) for an Rb87 atomic fountain clock. Compared with the conventional magneto-optical traps used in other clocks, our system is more robust, more compact, more stable, and saves about 60% laser power. This optical setup has operated for about a year in our fountain system, passed the thermal cycle tests and the mechanical vibration and shock tests, and maintained a high performance without a need for realignment.
We report on a widely tunable, narrow linewidth operation of a Tm:YAG ceramic laser. A volume Bragg grating is used in the cavity as a folding mirror for wavelength selection. The wavelength is tuned from 1956.2 to 1995 nm, leading to a total tuning range of 38.7 nm. The linewidth is around 0.1 nm over the whole tuning range. A maximum output power of 1.51 W at 1990.5 nm is achieved at 37.8 W absorbed pump power. Different saturation behaviors are observed in the laser performances at different wavelengths.
In laser-arc double-sided welding, the spectral characteristics of the arc plasma are calculated and analyzed by spectroscopic diagnosis. The results show that, compared with conventional tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, the introduction of a laser changes the physical characteristics of the arc plasma regardless of whether laser plasma penetration takes place, and that the influence of the laser mainly affects the near-anode region of the arc. When the laser power is relatively low, the arc column tends to compress, and the arc spectral characteristics show no significant difference. When the arc root constricts, compared with pure TIG arc, the electron density increases by ~2.7 times and the electron temperature decreases by ~3000 K. When the arc column expands, the intensities of spectral lines of both the metal and Ar atoms are the strongest. But it is also observed that the electron density reduces, whereas there is no obvious decrease of electron temperature.
Metals in nature exhibit a mediocre wettability and a high optical reflectance from the visible region to the infrared. This Letter reports that, by formation of nano- and microscale structures via a simple raster scanning of a focused femtosecond laser pulse without any further treatment, structured aluminum and nickel surfaces exhibit combined features of superhydrophobicity with a contact angle of 155.5°, and a high optical absorption with a reflectivity of several percent over a broad spectral range (0.2–2.5 μm). Thus, a multifunctional structured metal surface that integrates superhydrophobicity and a high broadband absorptivity has been easily realized by one-step femtosecond laser processing.
A laser-diode-pumped high-pulse-energy Nd:LiYF4 master oscillator power amplifier 1053 nm laser system is demonstrated. We design a home-made pump module to homogenize the pump intensity through the ray tracing method. To increase the extraction efficiency, the pre-amplifier adopts a double-pass amplification structure. At a repetition rate of 50 Hz, 655 mJ pulse energy and 12.9 ns pulse width of 1053 nm laser is obtained from the master oscillator power amplifier system. The corresponding peak power is 51 MW. The optical-to-optical efficiency of the system is about 9.7%.
High-quality holmium-doped Y3Al5O12 (YAG) ceramic is fabricated in sequence by tape-casting and vacuum sintering. The average grain size of the Ho:YAG ceramic is around 20 μm with a fully dense microstructure. The inline transmittance of the sample is ~82% in visible and IR region. The fluorescence lifetime at 2088 nm is 8.17 ms. The excellent properties of the Ho:YAG ceramic demonstrate the tape-casting is a novel candidate process for the fabrication of Ho:YAG-based thin-chip or composite ceramics.
Resonant effect is found in femtosecond laser ablating Pr–Nd glass. When processed with resonant wavelength of 807 nm, resonant ablation efficiency (RAE) with a single pulse can be improved by 45.22%. Furthermore, RAE closely relates to laser intensity. For resonant ablation, RAE is increased significantly when laser intensity <0.556×1014 W/cm2 at which multiphoton ionization dominates, while it fades away when laser intensity >0.556×1014 W/cm2 at which tunnel ionization dominates. Besides, it is also found that the ablation depth increases along with the wavelength rise when multiphoton ionization dominates, while the change rule is inversed when tunnel ionization dominates.
In this Letter, a gray-tracking-resistant—potassium titanyl phosphate (GTR-KTP) crystal is used for intracavity frequency doubling red laser generation for the first time. Under the 808 nm LD pump power of 180 W, as high as 12.5 W of red laser output is obtained with the optimum repetition rate of 7 kHz. Within the red laser power variation range between the maximum to 70%, a temperature tolerance is measured to be 35°C. The results prove that GTR-KTP should be a potential nonlinear crystal for red laser generation.
We report a direct, modulated bandwidth enhancement in a amplified feedback laser (AFL), both experimentally and numerically. By means of fabricated devices, an enhanced 3 dB bandwidth of 27 GHz with an in-band flatness of ±3 dB is experimentally confirmed at 13 °C. It is numerically confirmed that the modulated bandwidth of the AFL can be enhanced to two times its original bandwidth, with more controlled flexibility to realize a flat, small-signal response.
The combination of deep wet etching and a magneto-rheological finishing (MRF) process is investigated to simultaneously improve laser damage resistance of a fused-silica surface at 355 nm. The subsequently deposited SiO2 coatings are researched to clarify the impact of substrate finishing technology on the coatings. It is revealed that a deep removal proceeding from the single side or double side had a significant impact on the laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT) of the fused silica, especially for the rear surface. After the deep etching, the MRF process that followed does not actually increase the LIDT, but it does ameliorate the surface qualities without additional LIDT degradation. The combination guarantee both the integrity of the surface’s finish and the laser damage resistance of the fused silica and subsequent SiO2 coatings.
The generation and measurement of complex ultraviolet laser pulse shapes is demonstrated in the SG-III laser facility. Relatively high contrast ratio of 300∶1 required by the physics experiment is achieved and successfully measured. Two continuous main shots validate the reproduction and the stability of the pulse shape, which provide solid foundation for precise physics experiment and laser power balance.
A simple and repeatable method to fabricate high-aspect-ratio (HAR) and high-quality microgrooves in silica is reported. The method consists of two steps: (1) formation of laser-modified regions by femtosecond Bessel beam irradiation, and (2) removing laser-modified regions through HF etching. Uniform, straight microgrooves can be fabricated and the highest aspect ratio that can be reached is ~52. The phenomenon is attributed to the uniform energy distribution in the long propagation distance, which leads to the long and uniform laser-modified regions and subsequent HF acid etching of laser-modified regions with high selectivity. This method will have potential applications in fabrication of HAR microgrooves in transparent materials.
A stable three-channel dual-wavelength fiber ring laser is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The digital micromirror-device (DMD) processor can select and recirculate any dual waveband from the gain spectrum of the erbium-doped fiber at each channel. The uniform and stable dual-wavelength oscillation is obtained by a highly nonlinear photonic crystal fiber, which causes two degenerate the four-wave-mixing processes. By loading different reproducibility diffraction gratings on the optoelectronic DMD processor, the laser can be operated stably in a three-channel dual-wavelength scheme at room temperature. The power fluctuation of each laser channel is less than ~0.02 dB.
A ring of three unidirectionally coupled semiconductor lasers (RTUC-SLs) is used to generate broadband chaos with no pronounced time-delay (TD) signature. Using the autocorrelation function and permutation entropy as the TD measures, we demonstrate that under suitable coupling strength, the loss of the TD signature of the lasers in the RTUC-SL configuration is achieved both for the intensity and the phase. These findings should prove valuable for developing high-quality optical chaos for potential applications, such as chaos-based communications and random number generation.
A surprising phenomenon can be discovered by using femtosecond double-pulse ablation of silicon and germanium in ethanol. The ablation areas present an oscillation increase phenomenon when the pulse delay increases from 200 fs to 1 ps in the fluence range of 0.5–0.6 J/cm2. In contrast, the ablation areas exhibit an oscillation decrease phenomenon as the pulse delay increases when the laser fluence F<0.5 J/cm2, which is consistent with the results of the experiment in air. It is considered that the adjustment of the photon–electron coupling efficiency by pulse train technology plays an important role in the ablation process.
We report a 1.8 μm two-section distributed Bragg reflector laser using butt-jointed InGaAsP bulk material as the waveguide core layer. The threshold current is 17 mA and the output power is 8 mW on average. The threshold current, output power, and emitting wavelength dependences on temperature are measured. The obtained wavelength tuning range is 10 nm. This device has potential applications in simultaneous multiple-gas detection.
Stray light in high-power laser facilities not only decreases the gain capacity of the main amplifier, but can also cause permanent damage to optical components, greatly threatening the safety operation of the SG-III. This Letter reports a technique for quickly pinpointing the source of stray light in the main amplification optical path of the SG-III. The achieved results indicate that the accuracy of our method is up to 1 m in an optical path of 100 m. The judging method is effective for examining and removing harmful stray light in the SG-III laser facility and it can be promoted in huge laser facilities of this kind.
We report a simple Nd:YAG laser that emits radially polarized beam with helical wavefront. The laser cavity consists of a piece of laser crystal and a plane output coupler, and there is no additional polarization component inside it. The pump light is converted into annular profile through de-focal coupling into a multi-mode fiber. For the continuous-wave (CW) operation, the laser emits radially polarized vortex beam, and it is observed that the helical wavefront of the laser beam is switched from right handedness to left handedness when the output coupler is tilted slightly. For the Q-switched operation under the insertion of a Cr4+:YAG saturable absorber inside the cavity, we obtain radially polarized outputs with left-handedness helical wavefront. By tilting the laser crystal slightly, the laser output switches to azimuthal polarization at pump power larger than 4.5 W and left-handedness helical wavefront of laser beam is preserved.
Anisotropic dewetting polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surfaces, which consist of groove-like micro/nanostructures (so-called hierarchical structures), are fabricated using an ultrashort pulsed laser. The contact angles (CAs) are measured parallel to the microgrooves, which are always larger than those measured perpendicular to the microgrooves, exhibiting a superhydrophobic anisotropy of approximately 4° on these fabricated PDMS surfaces at optimized parameters. These pulsed-laser irradiated surfaces exhibit enhanced hydrophobicity with CAs that increase from 116° to 156° while preserving the anisotropic dewetting. Additionally, the wettability of the surfaces with different morphologies is investigated. The temporal evolution of the wettability of the pulsed-laser irradiated PDMS surface is also observed within the first few hours after pulsed laser irradiation.
A compact and stable all-normal-dispersion mode-locked ring fiber laser with the repetition rate of 312 MHz is obtained with a wavelength-division multiplexing isolator. The compressed pulse is nearly transform-limited and the pulse width is 118 fs. It exhibits an optical efficiency of 50% and the maximum output power is about 205 mW with a 410 mW pump.
This Letter proposes a method to balance the gain and loss of the orthogonally polarized emissions of dual wavelengths in a solid laser cavity. By adjusting the tilt angle of the uncoated glass plate inserted into the cavity, the gain and loss of the orthogonally polarized emission lines with small intervals can be balanced to equalize the oscillation thresholds of the orthogonally polarized dual wavelengths. We select the birefringent crystal Nd:LiYF (Nd:YLF) as the gain media, and theoretically analyze the simultaneous oscillation conditions of dual wavelengths with π- and σ-polarized emissions from a four-level transition (F3/24→I11/24 and F3/24→I13/24) in Nd3+. A simple linear cavity structure is adopted in the experiment, and stable CW orthogonally polarized dual-wavelength laser outputs of 1047, and 1053, 1321, and 1313 nm are obtained.
We fabricate a GaAs-based InGaAs/InGaAsP multiple quantum wells (MQWs) laser at 1.55 μm. Using two-step growth method and thermal cyclic annealing, a thin low-temperature InP layer and a thick InP buffer layer are grown on GaAs substrates by low-pressure metal organic chemical vapor deposition technology. Then, high-quality MQWs laser structures are grown on the InP buffer layer. Under quasi-continuous wave (QCW) condition, a threshold current of 476 mA and slope efficiency of 0.15 mW/mA are achieved for a broad area device with 50 μm wide strip and 500 μm long cavity at room-temperature. The peak wavelength of emission spectrum is 1549.5 nm at 700 mA. The device is operating for more than 2000 h at room-temperature and 600 mA.
We report an adjustable unbalanced quantum random-number generator based on the polarization of photons, which can produce nondeterministic true random unbalanced numbers. The underlying physical process is inherently quantum mechanical. To prove the quality of the output sequence of the proposed generator, we test the obtained bias-free sequence through the 3-standard-deviation criteria and the National Institutes of Standards and Technology test suite. Another type of nondeterministic unbalanced random-number generator is also studied in this work, to evaluate the quality of the output biased random numbers.
Owing to the small differences between the cross-sections of the four emission peaks around 1.3 μm, an efficient four-wavelength synchronous launched laser is demonstrated using a Nd:GdLuAG crystal. The laser has no special resonator design. The maximum output power is 4.28 W, which corresponds to a conversion efficiency of 45.6%. For the Q-switching, the laser operated in dual-wavelength mode, and the single pulse energy is maintained at ~80 μJ. By calculating the population inversion density, multi-wavelength emission characteristics in both continuous wave and Q-switching lasers are discussed.
We demonstrate a high-pulse-energy, short-pulse-width passively Q-switched (PQS) Nd:YAG/V3+:YAG laser at 1.3 μm, which is end-pumped by a pulsed laser diode. During the PQS regime, a maximum total output pulse energy of 3.3 mJ is obtained under an absorbed pump pulse energy of 21.9 mJ. Up to 400 μJ single-pulse energy is realized with the shortest pulse width of 6.16 ns and a pulse repetition frequency of 34.1 kHz, corresponding to a peak power of 64.9 kW. The high-energy laser pulse is operated in the dual wavelengths of 1319 and 1338 nm, which is a potential laser source for THz generation.
A depolarization phenomenon in an electro-optical crystal in a quasi-three-level 946 nm Nd:YAG laser is observed. A compensation of the thermal effects in electro-optical crystals is achieved by employing a quarter-wave plate, with one optical axis parallel to the laser polarization. This technique allows for the production of an electro-optically Q-switched 946 nm Nd:YAG laser at 1 kHz. A maximum output power of 350 mW at 1 kHz repetition frequency and 11 ns pulse duration are achieved with an output coupler of 10% transmission under the incident pump power of 11.1 W, corresponding to a peak power of ~32 kW.
We report, for the first time to our knowledge, a diode-end-pumped passively mode-locked (ML) Nd-doped gadolinium gallium garnet laser based on a chemically reduced graphene oxide (RGO) saturable absorber mirror. The ML laser gives a pulse duration of 15.1 ps under the maximum average output power of 1.44 W, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 21.1%. The single-pulse energy and peak power are 21.6 nJ and 1.43 kW, respectively. The results indicate that our RGO saturable absorber has promising prospects for applications in high-power and high-efficiency ultrafast lasers.
We propose and demonstrate a laser-diode-pumped, maglev rotating Nd:YAG disk laser. The disk of the laser crystal is attached to a maglev pyrolytic graphite disk and is rotated by compressed gas. In this rotating disk laser, the detrimental thermal effects are alleviated and the laser can be operated in the single transverse electromagnetic (TEM)00 mode with high brightness. In our proof-of-concept experiment, we achieve a 17.7 mW laser output at 447 mW of absorbed pump power and a ~4 Hz rotation frequency.
A high-power, high-energy Ho:YAG oscillator resonantly pumped by a Tm-doped fiber laser is presented. A maximum continuous output power of 38 W with a slope efficiency of 51.9% is achieved at the wavelength of 2.09 μm, and M2≈1.48. In the Q-switching regime, the maximum pulse energy of 12.8 mJ, corresponding to a 514.5 kW peak power, is obtained at the pulse repetition frequency of 1 kHz. Furthermore, the thermal lens effect of the system is studied theoretically, and the radius of the transverse electromagnetic (TEM00) mode of the laser crystal under different pump powers is given.
We report the experimental demonstration of transform-limited sub-6 fs pulses at an optimal central wavelength by a tunable noncollinear optical parametric amplification (NOPA) source. Meanwhile, a white light continuum in the near-infrared (NIR) range from 900 to 1100 nm is also successfully generated by focusing the unconverted 800 nm beam during NOPA generation on a sapphire rod. Both visible-pump/visible-probe and visible-pump/NIR-probe experiments are realized using the same laser system. As examples, ultrafast photo-induced exciton dynamics inside two kinds of materials are investigated by the visible-pump/visible-probe and visible-pump/NIR-probe spectroscopy, respectively.
In this Letter, we demonstrate a diode-pumped electro-optical cavity-dumped Tm:YAP laser for the first time to our knowledge. A pulse width of 7.1 ns is achieved at a wavelength of 1996.9 nm. A maximum output power of 3.02 W is obtained with a pump power of 58.8 W at a repetition rate of 100 kHz and a high-voltage time of 1000 ns, corresponding to an overall optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 5.2%. In addition, we study the effect of repetition rate and high-voltage time on the output power characteristics of a cavity-dumped Tm:YAP laser.
We experimentally and numerically demonstrate the generation of square pulses without any wave-breaking in a fiber ring laser. A segment of nonzero dispersion-shifted fiber is used to increase the laser cavity length and to optimize the parameters of the laser cavity. In the experiment, the pulse width can be tuned in a wide range from 13.5 to 119.5 ns without wave-breaking while the peak power remains almost constant. The maximum single-pulse energy is up to 65.58 nJ at a pump power of 508 mW. Numerical results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Numerical results also reveal the role of cavity length and nonlinearity in generating a square pulse without pulse breakup.
We demonstrate a diode-pumped picosecond Yb-doped silicate Yb3+:Sc2SiO5 (Yb:SSO) chirped pulse amplifier. The seed source with a pulse width of 220 fs is a diode-pumped Yb:KGW femtosecond oscillator. A single chirped volume Bragg grating is employed both as a pulse stretcher and as a compressor to improve the compactness of the system. Stretched pulse is amplified using a diode-pumped Yb:SSO regenerative amplifier. The maximum amplified pulse energy obtained at a pump power of 13.5 W is 450 μJ. The amplified pulse is centered at 1033.3 nm before compression at a frequency of 1 kHz. After compression, the pulse energy is 315 μJ with a pulse duration of approximately 1 ps.
We investigate the influence of environmental media on ablation rate of AISI 443 stainless steel under femtosecond (fs) laser single raster scan and multiple raster scans in air, water, and methanol. Meanwhile, the development of ablation rate with the change of fs laser-induced surface morphology in the three environmental media is comparatively studied. The results show that environmental media as well as fs laser-induced morphology control the ablation rate with the increasing number of raster scans (N). Under single raster scanning (N = 1), the ablation rate is higher in liquid than in air due to the confinement of plasma, laser-induced shockwaves, and bubble-related mechanical forces. However, under multiple raster scans, the variation in ablation rate with the increase in N in these three environmental media is complicated and is largely determined by the surface morphology induced by previous fs laser ablation. When N > 20, the ablation rate is much higher in air than in liquids due to preferential ablation caused by the formation of nanostructures-textured mound-shaped microstructures in air. Besides, the redeposition of ejected ablated materials is also an important factor that affects the ablation depth.
We demonstrate time-division-multiplexing (TDM) laser seeded optical amplification in a diode laser amplifier. With an acousto-optic modulator we combine two seeding beams of different frequencies and inject them alternately in the time domain into the tapered amplifier (TA) chip at a switching speed of 200 ns. The output high-power dual frequency components from the TA are time separated. The TDM seeded TA works safely and efficiently, which is useful for compact precision measurement instruments such as optical clocks and atom interferometers.
A speckle pattern is observed when a neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser is homogenized by a diffractive optical element (DOE) due to its high spatial coherence. Therefore, a Nd:YAG laser homogenized by a DOE was previously considered not suitable to pump a Ti:sapphire laser amplifier. However, we show by experiment and simulation that the speckle structure does not manifest itself in the final amplified Ti:sapphire laser beam. By using the homogenizer, a smooth distribution of the amplified laser beam is obtained. No degradation of the energy, the wavefront, and the temporal characteristics of the amplified laser beam is observed.
In this article, we analyze the factors that limit the output power increase for photonic crystal fiber lasers and set a theoretical model to calculate the maximum extractable power of ytterbium-doped photonic crystal fibers. Numerically, when the diameter of core is 76-\mu m and the pumping intensity is 0.21 W/(\mu m2×Sr), the output of pure silica and ytterbium-doped photonic crystal fiber lasers is 100-kW, considering the technology for the time being. The main limitations of power scaling are facet damage and thermal self-focusing. In case of the strict single-mode operation condition, the maximum extractable power is 100-kW when the numerical aperture is 0.05. Considering the strict single-frequency operation condition, the maximum extractable power of both pure silica and ytterbium-doped photonic crystal fiber lasers is 1.65-kW, where the main factor is stimulated Brillouin scattering effect. Compared with the previous results, the increase in the maximum extractable power depends on three parameters: the availability of high-brightness pump diodes, the endless single-mode characteristic of the photonic crystal fiber, and the high doping density which lead to efficient absorption coefficient of pumping light. Finally, we simulate numerical aperture that influences the maximum power of photonic crystal fiber lasers and compare the difference in maximum output power of photonic crystal fibers and double-cladding fiber lasers in single-frequency condition.
Random distributed feedback Raman fiber laser is a convenient method to generate laser without using cavity mirrors. We show for the first time to the best of our knowledge a 10-W-level random fiber laser operated at 1178 and 1212 nm (1.2-μm range). The power character and features in time domain and spectrum are presented.
To study how laser pulse wavelength will affect the damage characteristics of optical elements with different degrees of contamination, we compare the extent of damage on optical glass between nanosecond pulsed laser of 1064 and 355 nm wavelength, respectively, and reach the following conclusions: the surface quality of clean optical elements determines its own anti-laser damage capability; the damage probability of optical sample caused by ultraviolet radiation-induced organic contamination is much higher than the infrared radiation-induced one; and contaminated metal particles can lower damage threshold of optical elements by 2–3 times.
We propose a method of cascading multiple nonlinear optical loop mirrors (NOLMs) in the laser cavity to enhance the single pulse energy in mode-locked fiber lasers. A geometrical description is used to engineer the transmittance curve of the effective mode locker in the cavity to enlarge the threshold of triggering multipulse transition. A full vector model of Ginzburg–Landau equation is adopted to model the pulse evolution in the cavity. Results show that, with the cascading NOLMs configuration, the single pulse energy and peak power can be increased by 170%–188% comparing with that in single NOLM cavity.
In order to research the influence on the beam transmission properties due to the different time intervals in the high-power pulsed transversely excited atmospheric CO2 laser with unstable resonator, the finite element analysis of thermodynamics instantaneous method are adopted to analyze the mirror thermal deformation irradiated by the high-power laser beam. The mirror thermal deformation is fitted by Zernike polynomials. Then the angular spectrum propagation theory of diffraction is used to calculate the far-field transmission properties. The simulation results show that with the decrease in the time interval between each pulse, the mirror temperature and thermal deformation gradually increase, and peak power and the average energy density decrease, and beam broadens. With the 500 Hz repetition rate relative to the 10 Hz repetition, the peak intensity decreases almost 40%; the optical spot broadens about 60%. When the repetition rate is larger than 100 Hz, the surface of mirror will have obvious deformation, which will cause apparent degradation in the optical beam quality for the far-field transmission.
We report a diode-end-pumped Q-switched YVO4/Nd:YVO4/YVO4 self-Raman second-Stokes laser at the wavelength of 1764 nm. With the incident pump power of 32 W and the pulse repetition frequency of 20 kHz, the maximal average output power at 1764 nm is up to 1.18 W, with the corresponding optical conversion efficiency of 3.69%. The highest pulse energy and peak power are 59 mJ and 31.7 kW, respectively.
We demonstrate a narrow linewidth 1881 nm Tm:YAG ceramic laser that combines the advantages of in-band pumping at 1617 nm and volume Bragg grating as a wavelength selection device. With an output coupler of 5% transmission, a maximum output power of 200 mW is obtained at 1881 nm with a linewidth of 0.2 nm.
Distributed feedback fiber lasers with multiple phase shifts are fabricated and investigated. Single longitudinal mode lasers with single polarization are obtained by the structure design with two phase shifts. No obvious differences in laser performance, including pump threshold, slope efficiency, relative intensity noise, spectral linewidth, and polarization state, are observed for the presented distributed feedback fiber laser structures with different phase shift locations.
A Q-switched Er-doped all-fiber laser, based on a single-walled carbon nanotube saturable absorber (SA) is constructed. The SA with a modulation depth of 8% is prepared using a special chemical-corrosion method. Furthermore, the SA is introduced to an Er-doped all-fiber laser, and Q-switching is obtained successfully. The repetition rate of the Q-switched laser can be tuned continuously from 128 to 278 kHz with pulse widths from 1.92 μs to 488 ns. The maximum output power is 13.1 mW.
In order to study the beam cleanup effect of the stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) in the graded-index multi-mode fiber (GIMF), a continuous wave all-fiber laser at 1117.8 nm and a pulsed fiber amplifier at 1064 nm are built up as the seed and pump source in the Raman fiber amplifier (RFA). In unseeded SRS process, a pump beam with M.2x = 6.7 and M.2y = 6.7 is transferred into a Stokes beam with M.2x = 1.5 and M.2y = 1.7 in the multi-mode fiber with a 62.5 μm graded-index core (numerical aperture =0.29). In the RFA, a seed light with M.2x = 6.7 and M.2y = 7.3 is amplified to a signal light with M.2x = 1.8 and M.2y = 2.0. The experimental results are explained by the simulation on the mode evolution during SRS procession and Raman amplifica-tion in the GIMF. The results show that both the SRS and Raman amplification effect in the GIMF have beam cleanup effect.
Fe-Mn-Si-Cr-Ni composite powders are utilized to form a functional shape memory alloy cladding layer (SMACL) using a laser cladding method. The microstructure, microhardness, and phase composition of the SMACL are measured, and the extent of deformation of the laser cladding samples is determined. The SMACL is composed of planar, cellular, and dendritic crystals, equiaxed grains, and oxides with increasing distance from the substrate surface. The SMACL is further composed of \varepsilon -martensite and \gamma -austenite phases, while the tempered SMACL consists mainly of \gamma -austenite. Extensive deformation occurs in AISI 304 stainless steel laser cladding samples. By contrast, limited deformation is observed in the SMACL samples.
We report a line-narrowed electro-optic periodically-poled-lithium-niobate (PPLN) Q-switched laser with intra-cavity optical parametric oscillation using a grazing-incidence grating, producing 8-ns, 5-\mu J pulses at 10-kHz repetition rate when pumped with a 10-W diode laser at 808 nm. The output wavelength is centered at 1554.3 nm with a 0.03-nm spectral width. Wavelength tuning is achieved by rotating a mirror and changing the crystal temperature.
Optical tweezers with a low numerical aperture microscope objective is used to manipulate the microspheres at the water-air interface. In this letter, we determine the optimal optical trap for the lateral manipulation of microspheres at a water-air interface. The experimental results show that the trapping force is influenced by the expansion of the trapping beam at the back aperture of the objective. The optimal filling ratio of 0.65 is suggested for lateral optical manipulation at the water-air interface. The lateral trapping forces at the water-air interface are theoretically investigated with the ray-optics model. The numerical results show that the lateral trapping forces can be changed by shrinking the diameter of the trapping laser beam. The numerical results are in accordance with the experimental results.
Graphene saturable absorber (SA) is used as the passive Q-switcher of a 0.9-\mu m solid-state laser. When the laser medium is a Nd:La0.11Y0.89VO4 crystal, the initial transmittance of the graphene SA is 78%; at an absorbed pump power of 7.62 W, the maximum average output power, largest pulse energy, and minimum pulse width are 0.62 W, 2.58 μJ, and 84 ns, respectively. This study shows that graphene is a promising and cost-saving SA for 0.9-\mu m pulse generation.
A mode locked Er-doped fiber laser based on a single-wall carbon nanotube saturable absorber is demonstrated. A high quality single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) absorber film is fabricated by a polymer composite. The pulse duration is 488 fs with 9.6-nm spectral width at the center of 1564 nm. The repetition rate is 30.4 MHz. The maximum output power is 3 mW. And the single pulse energy is 0.1 nJ.
In this letter, the influence on the beam quality due to cumulative effect of the inner channel thermal deformation in the high energy laser system with unstable resonator is researched. Firstly, three typical laser powers of 50, 100, and 150 kW are selected to analyze thermal deformation of mirror by the finite element analyze of thermodynamics instantaneous method. Then the wave front aberration can be calculated by ray-tracing theory. Finally, Strehl ratio and Zernike aberration coefficients of the vacuum far-filed beam can be calculated and comparably analyzed by Fresnel diffraction integration. The theory and simulation results show that due to the effect of inner channel thermal deformation, eccentric phenomenon and astigmatism of far-filed beam emerge, and peak power and the focused ability decrease. With the increasing of reflective times, Strehl ratio decrease, and tilt, astigmatism and coma of x direction gradually increase, which become the main aberration. The results can provide the reference to the thermal aberration analysis for high energy laser system and can be applied to the field of laser nuclear fusion and laser weapon, etc.
Three-dimensional (3D) simulations and theoretical analyses on super-short pulse generated using freeelectron lasers (FELs) at perfect synchronism are carried out with the help of our 3D OSIFEL code. The evolution of longitudinal pulse width in the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) experiment is simulated. The results show that the optical pulse is compressed on successive passes due to the slippage between the optical and electron beams, and an ultra-short 221-fs optical pulse is finally obtained, which agrees with the experiment. Furthermore, to shorten wavelength such as soft ultraviolet (SUV) spectrum range, an ultra-short pulse generated at perfect synchronism is analyzed and studied. Finally, the relationship between the optical pulse length compressed and the peak electron beam current is calculated. It shows that the higher the electron beam current, the shorter the output FEL width length, due to the higher gain.
Core-diameter adjustment, in analogy to doping management, is proposed in this letter for balancing thermal load and nonlinear effects. In this scheme, the core-to-cladding ratio increases with increasing core diameter along the direction of signal and pump propagation. An all-fiber-integrated Yb-doped master oscillator power amplification (MOPA) is successfully demonstrated. Two segments of fiber with different core diameters but same inner-cladding diameters and doping levels are spliced together and used as gain fibers in the last stage. A maximum average output power of 200 W at an overall slope efficiency of 71% is achieved from the MOPA with a pulse energy of 2 mJ and peak power as high as 80 kW.
The quantum cascade laser (QCL), a potential laser source for mid-infrared applications, has all of the advantages of a semiconductor laser, such as small volume and light weight, and is driven by electric power. However, the optical power of a single QCL is limited by serious self-heating effects. Therefore, beam combination technology is essential to achieve higher laser powers. In this letter, we demonstrate a simple beam combination scheme using two QCLs to extend the output peak power of the lasers to 2.3 W. A high beam combination efficiency of 89% and beam quality factor of less than 5 are also achieved.
A compact Er:fiber ring laser operated at a fundamental repetition rate of 325 MHz is reported. Two gain fibers with opposite dispersion are employed to shorten the fiber laser cavity for high repetition rate and soliton-like pulse generation without losing gain and compactness. The spectral bandwidth of the output pulse is 24 nm and the direct pulse duration is 123 fs without extra-cavity compression, which are values near the transform-limited range.
We investigate InAs/GaAs quantum dot (QD) lasers grown by gas source molecular beam epitaxy with different growth temperatures for InAs dot layers. The same laser structures are grown, but the growth temperatures of InAs dot layers are set as 425 and 500 oC, respectively. Ridge waveguide laser diodes are fabricated, and the characteristics of the QD lasers are systematically studied. The laser diodes with QDs grown at 425 oC show better performance, such as threshold current density, output power, internal quantum efficiency, and characteristic temperature, than those with QDs grown at 500 oC. This finding is ascribed to the higher QD density and more uniform size distribution of QDs achieved at 425 oC.
In order to meet high pulse laser output, the laser shock power supply based on insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) inverter technology, constant current-constant voltage charger mode, high voltage pulse spark, and high pulse current discharger technology is designed. The master oscillator stage and two amplifier stages for xenon flash lamp spark and discharge circuits are designed in this power supply. The voltage of energy storage capacitors can be adjusted from 1 000 to 3 000 V. A variety of measures, such as FREE and Q-switch mode, trigger signal delay, water confining layer control, cooling water control are provided for laser shock processing technology optimization.
Nd0.02Y1.78La0.2O3 transparent ceramic is fabricated by conventional ceramic sintering process. The transparent ceramic has excellent spectroscopic properties, with the absorption cross section of 1.53×10-20 cm2 and broad full width at half maximum (FWHM) of about 8 nm at 806 nm, the emission cross section of 3.57×10-20 cm2 at 1 078 nm, and the decay lifetime of 232 \mu s. For Nd0.02Y1.78La0.2O3 ceramic laser, a maximum continuous wave (CW) laser output power of 1.38 W with a slope efficiency of 22.9% is obtained at 1 079 nm under an 808 nm diode pump.
A method with a simple configuration is demonstrated to narrow the spectrum line-width of the fiber lasers. The configuration consists of one coupler and four fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs). The number of longitudinal modes is decreased significantly using multi-cavities by comparing multi-cavities configuration with single-cavity configuration. The spectrum line-width is effectively narrowed. The whole system is simple in technology and low in cost.
5 at.-% Yb3+ doped (La0.10Y0.90)2O3 transparent ceramics are fabricated by using commercial nanopowders in H2 atmosphere. Effect of the heat-treatment on the structure, spectral properties of (Yb0.05La0.10Y0.85)2O3 transparent ceramics is investigated. Laser grade ceramic samples are fabricated, and a diode-pumped laser is demonstrated, the maximum output power of 920 mW at 1 075 nm is obtained with a slope efficiency of ~31%, the laser pulse as short as 730 fs is also realized at the central wavelength of 1 033 nm.
We demonstrate a passively Q-switched Tm-doped fiber laser with carbon nantubes (CNTs), yielding a maximum output average power of around 82 mW and the corresponding pulse energy of 1.2 \mu J. The laser operates at ~1.985 \mu m with repetition rates ranging from 26 to 69 kHz and pulse-duration from 1.5 to 2.6 \mu s. Our proposed laser shows that the CNTs are promising for the potential Q-switched Tm-doped fiber laser with high energy and tunable wavelength operation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a Q-switched Tm-doped fiber laser with CNTs as saturable absorber.
We present a wave-front sensor-less adaptive optics (AO) system for a Nd:YAG Zigzag slab amplifier. A 39-element rectangular piezoelectric deformable mirror in combination with a stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm is introduced for both static and thermal aberrations correction. Preliminary experiments demonstrate that the output beam quality can be enhanced greatly at different power levels.
Laser shock processing (LSP) is an innovative surface treatment technique with high peak power, short pulse, and cold hardening for strengthening metal materials. This process induces intensive plastic deformation and deeper compressive residual stress and improves the surface performance of materials. The titanium alloy of TC4-DT is the important materials in many industry fields including aviation, which is used widely on hole and welding structure. However, the researches of surface treatment on TC4-DT welding structure using LSP technology are seldom reported by now. The performances of TC4-DT, including mircrohardness and surface profiles, are improved through the technology of LSP.
A laser micromachining technique for the fabrication of metallic microstructures is proposed. The fabrication of microstructures is done by laser-induced wet etching that adopts an optical fiber as a machining tool. The laser beam delivered through the multimode fiber directly irradiates on the workpiece while maintaining a proper gap to avoid fiber damage. The manufacture of microstructures with high surface quality and good size uniformity is realized. Microgrooves with aspect ratio over 10 and microholes with a nearly straight cross-section can be produced by the proposed technique. The overall etching results are examined closely with respect to process variables.
To resolve the variability of the intensity distribution and the divergence of the laser diode (LD) output beam in a beam shaping system, a diffractive optical element (DOE) array is proposed in LD beam shaping. This DOE array can divide the wavefront of input beam. All light diffracted by all DOE array units is super-positioned on the output plane, and the tolerance for the input beam is improved by this means. Using the above DOE array laser shaped method, three rectangles intensity distribution are realized from Gaussian beam with the diffraction efficiency of 90.5% and the uniformity of 96%. When the half divergence angle of the LD varies from 2o to 16o in slow and fast axis directions, respectively, the diffraction efficiency maintains to be approximate 90% and its uniformity is more than 95%. When the defocus of the lens to collimate LD beam varies from -32 to 32 \mu m, numerical experiments indicate that uniformity and the diffraction efficiency of the shaped beam by the DOE array do not vary.
The phase aberrations caused by thermal deformations is one of the main limitations in a beam control system. If left uncorrected, it would significantly reduce the effectiveness of high-power lasers as devices for beaming power over long paths through the atmosphere. For the purpose of overcoming the effects of phase aberrations, the method of conjugation wavefront pre-compensation of incident laser is introduced and theoretically studied. Based on the simulated results of thermal deformations at different irradiations time, choosing the power in the bucket (PIB), Strehl ratio, and the root-mean-square of phase as the characteristic parameters, the beam quality of emitted laser with and without wavefront pre-compensation is calculated respectively and compared. The result shows that under the condition that the conjugation compensation phase is placed on the incident beam, the beam quality of emitted laser is ameliorated prominently especially for a beam control system with serious thermal deformations.
Periodic nanostructures spaced by half of the wavelength can be obtained by the technology of laser-focused atomic deposition. Experimental result with single standing wave layer is presented, with a periodicity of 213 ± 0.1 nm, a height of 4 nm, and a feature width of 64 +-6 nm. To further minimize the feature width,focusing and depositing characteristics of double standing wave layers are numerically simulated with optimized particle optics model. It is shown that the spherical aberration is reduced significantly. The predicted feature width is 18.2 nm and the height is approximately 12.6 nm when the powers of the two standing wave layers are 6 and 14 mW, respectively. Well-defined line occurs even when the full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of transverse angular spread reaches 0.5 mrad.
Carrier-envelope phase effect of the monochromatic high frequency pulse generation from Thomson backscattering is investigated with an analytical model and verified by one dimensional particle in cell simulations. We show that the central frequency of the monochromatic light generated from Thomson backscattering is extremely sensitive to the carrier-envelope phase of the field driving the relativistic electron layers.
The single cavity all-dielectric thin film Fabry-Perot filter (s-AFPF) is investigated in this letter as a means of tuning the wavelength in an external cavity diode laser (ECDL), and the means of limiting longitudinal mode hopping is also investigated. When a TE or TM plane wave irradiates a s-AFPF, a quasilinear relationship is found in a certain wavelength range between the optical intensity peak-transmittance wavelength of s-AFPF and the cosine value of plane wave incident angle at s-AFPF. Based on this feature, we propose and investigate a configuration with a s-AFPF in a tunable ECDL. By theoretical calculation, a mode-hop-free wavelength tuning range of ~5 nm around 1 550 nm is achieved. The ECDL can be used in the application of environmental monitoring, atomic and molecular laser spectroscopy research, precise measurements, and so on.
A diode-pumped picosecond mode-locked Yb:YAG ceramic laser is realized with a slope efficiency of 44%. Output power up to 1.04 W is obtained with pulse duration of 10.4 ps at central wavelength of 1 049.5 nm. The standard deviation of maximum output power instability is 0.00453.
Different distributed feedback (DFB) configurations in optically pumped polymer lasers, including the active Bragg grating structures, the dielectric grating structures spin-coated with polymeric semiconductors, and the actively waveguide dielectric grating structures (AWGS), are studied systematically. In the experiment, the F8BT polymer poly [(9,9- dioctylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl)-alt-co- (1,4-benzo-{2,1’,3} -thiadiazole)] is employed as the active medium in the three laser configuration. And all grating structures are fabricated though interference lithography or interference ablation. It is found that the AWGS design has advantages over the other two. The continuous and high-quality active waveguide in the AWGS enables low-threshold (115 \mu J/cm2) laser emission with narrow linewidth (~0.4 nm at full-width at half-maximum). The experimental verifications are in good agreement with the theoretical analysis. These results reveal some interesting mechanisms in optically pumped DFB polymer lasers, and it may be enlightening to the construction of electrically driven organic lasers.
In order to investigate the effect of multi-micro laser shock peening on residual stress of copper materials, surface residual stress is measured, and distribution of residual stress under different overlapping rates and laser energies is explored. Surface mean residual stress is proposed as characteristic means according to the defect of test equipment in existence. Numerical simulation is carried out to display residual stress distribution on top surface and depth in the overlapping process of microscale laser peening. The results show that overlapping rate and laser energy greatly influence the distribution of residual stress, and the surface mean residual stress is an effective characteristic means according to the residual stress distribution along typical paths and mean stress formula.
Highly efficient passively Q-switched Yb:YAG ceramic laser with Cr4+:YAG crystal as saturable absorber is achieved. Maximum average output power of 0.96 W is obtained when the absorbed pump power of 3.8 W is used; corresponding optical-to-optical efficiency is about 25%. The slope efficiency is 30%. Laser pulses at 1 030 nm with pulse energy of 107 μJ and pulse width of 9 ns are achieved at repetition rate of 9 kHz, with corresponding peak power of 11.9 kW. Meanwhile the effects of absorbed pump power on the characteristics of passively Q-switched laser pulses are investigated systematically.
Axial multiple foci patterns of radially polarized hollow Gaussian beam (HGB) with radial wavefront distribution is investigated theoretically. The wavefront phase distribution is cosine function of radial coordinate. Simulation results show that the multiple foci patterns can be adjusted considerably by the beam order of HGB and cosine parameter that indicates the phase change degree. The foci number fluctuates on increasing cosine parameter for certain beam order. And when the beam order is small, there occur five foci in focal region, and the cases are more frequently than that under the condition of higher beam order. Gradient force distributions are also given to show that the multiple foci of radially polarized HCB may be applied to construct tunable optical traps.
We report on extra cavity frequency doubling lasers for 266 nm with a compact, tunable extended cavity diode laser (ECDL) at 1 064 nm. The ECDL injected into a tapered amplifier yields a power of 290 mW. In a first frequency-doubling stage, about 47-mW green light at 532 nm is generated. Subsequent second-harmonic generation (SHG) employing a BBO crystal leads to about 30 μW of ultraviolet (UV) light at 266 nm. The tunable characteristic of this UV light source is discussed. The tuning span of quasi-phase matching of doubling cavity for 532 nm with PPKTP crystal is achieved with –3.5 nm by changing the temperature of PPKTP and is achieved with –1.186 nm by adjusting angle of PPKTP.
A fiber laser system emitting high-quality ultrashort powerful light pulses is reported. The photonic crystal fiber featuring high-gain large -mode-core and short absorption length is used, and the fiber laser is passively mode-locked by a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror. Its output greatly exceeds the power limitation of single-mode fiber oscillators with 1.4-W average power at 1 039-nm center wavelength, 6.9-ps pulse width, and 45.4-MHz repetition rate.
We demonstrate a diode-pumped master-oscillator/fiber-amplifier (MOFA) system consisting of a passively SESAM mode-locking Nd:YVO4 laser and a Yb-doped large-mode-area fiber amplifier, which generates total average power of 24.4 W at 1 064 nm center wavelength, 91.5 MHz repetition rate, and 21.9 ps pulse duration. Power scaling limitations that arise from nonlinear distortions such as self-phase-modulation (SPM) and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) have not been observed during the whole experiments.
Thermal depolarization caused by birefringence is a major factor that limits the output power of linearly polarized Nd:YAG laser. This paper theoretically analyzes the thermal depolarization of [111]- and [100]-cut Nd:YAG rods and output power of two diode-pumped Nd:YAG rods are compared experimentally. 3×80 mm sized [111]- and [100]- cut rods with doping concentration of 1.1±0.1at.% are used. With a pump power of 180 W, the ratio of linearly polarized output power versus unpolarized output power obtained with the [111]- and [100]- cut rods are 19% and 43% respectively, with a difference of 24%. The experiment demonstrates that in comparison with conventional [111]- cut Nd:YAG rod, [100]- cut Nd:YAG rod can improve the linearly polarized output power obviously. The thermal depolarization depends on the polarization direction for the [100]- cut Nd:YAG rod, and the linearly polarized output power can be improved by suitably modification of the polarization direction of linearly polarized laser to minimize thermal depolarization.
A high power and good beam quality InGaAs/GaAs quantum well semiconductor disk laser at 1 015 nm wavelength is reported. The semiconductor wafer is grown in reverse order: substrate is on the window side and the distributed Bragg reflector is the last grown epilayer. Then the wafer is up-side-down and capillary bonded to a SiC heatsink, and the substrate is chemically etched. Because the total thickness of the substrate-removed structure is less than 10 μm, the thermal management of the laser is significantly improved, and the maximum output power over 0.6 W is obtained using a 3% output coupler and 3.2 W incident pump power. The M2 factors of 1.02 and 1.01 indicate a near-diffraction-limited beam quality. To further reveal the characteristics of this substrate-etched structure on the thermal management, the heat flux and the temperature distribution of the gain wafer are numerically analyzed, and the corresponding results are discussed.
A diode-side-pumped Tm,Ho:LuLiF laser at 2-1m wavelength obtained in a ring resonator and its amplification experiment are reported. At the maximum pump energy of 4.7 J available for the oscillator, the output energy per pulse for the oscillator decreases from 904 to 483 mJ in free running mode, and decreases from 106 to 68 mJ in Q-switched mode, with an increase of pump pulse repetition rate from 1 to 5 Hz. When considering the amplifier, 99-mJ Q-switched output energy is achieved at 5-Hz repetition rate.
Diode-end-pumped continuous-wave (CW) Tm:YAP and Tm:YLF slab lasers are demonstrated. The a-cut Tm:YAP and Tm:YLF slabs with doping concentrations of 4 at.-% and 3.5 at.-%, respectively, are pumped by fast-axis collimated laser diodes at room temperature. The maximum CW output powers of 72 and 50.2 W are obtained from Tm:YAP and Tm:YLF, respectively, while the pump power is 220 W, corresponding to the slope e±ciencies of 37.9% and 26.6%, respectively.
A nanosecond square pulse fiber laser based on the nonlinear amplifying loop mirror (NALM) is numerically analyzed by the nonlinear Schr¨odinger equation. The fiber cavity with a NALM has a tendency to provide pulse shaping effect with nonlinearity increasing in the NALM, and the nanosecond square pulse is generated by the pulse shaping effect. The numerical results show that the stable square pulse can be obtained when the parameters of the NALM are chosen appropriately. The generated square pulses have flat top and no internal structure.
A method of locking the relative phase to provide stable constructive or destructive interference between the phase-modulated sidebands from a pair of phase modulators is demonstrated. It is discussed theoretically for optimal fringe visibility related to the phase noise from faulty system. After phase locking using the phase modulating and lock-in technique, the drift of the relative phase is focalized around +-0.0016 rad and the fringe visibility is restricted to 2×10?4.
A laser power feedback control system that features fast response, large-scale performance, low noise, and excellent stability is presented. Some essential points used for optimization are described. Primary optical lattice experiments are given as examples to show the performance of this system. With these performance characteristics, the power control system is useful for applications in cold atom physics and precision measurements.
Ba impurity in potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) is studied with the first-principle simulation method. The relaxed configurations and density of the states of KDP crystal with Ba impurity are calculated. We find that Ba can generate a K vacancy and an interstitial O-H unit for charge compensation. The band gap of KDP crystal narrowed down to about 3.9 eV, which is consistent with the experimental data from previously reported studies and indicates that Ba may be a source of low-damage threshold.
We report a 1 018-nm ytterbium-doped double-clad fiber laser pumped by 970-nm diode. A pair of fiber Bragg gratings with reflectivities of 99.9% and 9% at a center wavelength of 1 018.9 nm are employed as cavity mirrors. The ytterbium-doped double-clad fiber is a 2.6-m-long Liekki fiber. Laser output power of 7.5 W at 1 018 nm is obtained under the pump power of 59.2 W. The overall slope efficiency of the fiber laser is about 16%. This low slope efficiency is mainly due to the incomplete absorption of the pump power.
A novel beam-steering external cavity diode laser using an intracavity lead lanthanum zirconate titanate (PLZT) electro-optic ceramic deflector is proposed and demonstrated experimentally. The laser consists of a semiconductor laser with single mode fiber coupled output, polarization controller, PLZT electro-optic ceramic deflector, and output concave mirror. By applying proper driven electrical signals on the PLZT electro-optic deflector, the beam deflection angle achieves 5.8 mrad at 1 000 V. A high-speed beam-steering property with less than 120-ns switching time is also observed. Moreover, a good beam quality with Gaussian spatial profile and a linear polarization state are obtained.
A conductively cooled, laser diode (LD) end-pumped, injection-seeded single-frequency Nd:YAG laser is designed and implemented. The laser is capable of producing an 8-mJ Q-switched pulse with a 11-ns pulse width at 1 064 nm and at a pulse repetition rate of 1 000 Hz. At the maximum output energy of 8 mJ, the frequency jitter is less than 3.5 MHz (root mean square (RMS)) over two minutes, and the linewidth is around 54.2 MHz. The M2 of the laser beam is approximately 1.30 in both horizontal and vertical directions. The optimized ramp-fire technique is applied to build reliable single longitudinal mode oscillating.
A compact high-power picosecond regenerative amplifier based on continuous wave (CW) diode side-pumped Nd:YAG is demonstrated. Average power of 8.8 W is achieved at a repetition rate of 5 kHz at a wavelength of 1 064 nm with a pulse duration of 28 ps, corresponding to a pulse energy of 1.76 mJ and a peak power of 62.9 MW. The beam quality is close to the diffraction limit with M2x = 1.24, M2y =1.03. To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest pulse energy obtained from a CW diode pumped Nd:YAG picosecond regenerative amplifier.
The chemiluminescence spectrum in the optical cavity of discharge-driven hydrogen fluoride (HF) chemical laser is measured. The result reveals that the spectra of the helium and fluorine (F) atoms are the major components. Moreover, the green chemiluminescence in the downstream of the optical axis is mostly composed of the 60P20 spectral line of the HF molecule. The analysis shows that, except for the cold pumping reaction, the recombination of the F atoms and the hot pumping reaction also occur in the optical cavity. Due to the hot pumping reaction and the optical cavity temperature in a specific range, the 60P20 line becomes the strongest HF molecule in the downstream region of the optical axis. After the hot pumping reaction, the green chemiluminescence always appears in the downstream region of the optical axis when the optical cavity temperature varies in a greater range.
A laser diode-pumped high-efficiency widely tunable Tm:YAP laser with excellent comprehensive properties is reported. The output power is stable at a given pump power. Under the absorbed pump power of 12.95 W, the maximum output power at 2,010 nm is 5.16 W, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 45.5%. The generated beam profile is close to the Gaussian TEM00 near the maximum pump power. Furthermore, the laser working wavelength can be continuously tuned through optimization from 1,894 to 2,066 nm, which is the widest tunable range for Tm:YAP lasers to date.
With a plano-concave cavity, diode-pumped continuous-wave (CW) and actively Q-switched Nd:YVO4 laser operating at 1.34 \mu m is demonstrated. Maximum CW output power of 4.76 W and Q-switched average output power of 2.64 W are obtained with output coupler (transmission T=3.9%). For the Q-switching operation, the theoretically calculated pulse energy and pulse width, with a pulse repetition frequency (PRF) range of 5–40 kHz, coincide with the experimental results. With a T=11.9% output coupler, the maximum peak power of 24.3 kW and minimum pulse width of 6.5 ns are obtained when the PRF is 10 kHz. To the best of our knowledge, this is the shortest actively Q-switched pulse duration ever obtained in a 1.3-\mu m Nd-doped vanadate laser.
An efficient high-power diode-pumped femtosecond Yb:KGW laser is repored. Through optimization of energy density by semiconductor saturable absorber mirror, output power achieved 2.4 W with pulse duration of 350 fs and repetition rate of 53 MHz at a pump power of 12.5 W, corresponding to an optical-to-optical efficiency of 19.2%. We believe that it is the highest optical-to-optical efficiency for single-diode-pumped bulk Yb:KGW femtosecond lasers to date.
An ultrabroadband supercontinuum (SC) is demonstrated in a pure silica photonic crystal fiber (PCF) pumped by quasi-continuous wave nanosecond-long pulses at 1,064 nm. The generated SC spectra extending from 450 to at least 2,400 nm have the salient feature of a short wavelength regime below the pump wavelength, which is much higher in intensity than the long-wavelength over the pump wavelength. The influence of pump power and repetition rates on SC generation (SCG) is explored. Results suggest that this pump source has both the advantages of short-pulse and continuous-wave pumps for SCG.
In this letter, a thin slab of glass is used as Fabry–Perot etalon inside a cavity of a continuous wave (CW) Nd:YAG laser to change the behavior of its output longitudinal modes. The slab etalon is used as tuning element when it turns around the laser cavity axis. Two simultaneous longitudinal modes with a relatively wide tuning range from 5.83 MHz to 0.02 THz are obtained when the Nd:YAG laser is operated at moderate output power of about 120 mW. The mode structure of this configuration is modeled and simulated. Computer-generated diagrams are also presented schematically and compared with the experimental results.
By aiming the pump wavelength of the laser diode to the absorption peak at 811 nm of the (Nd0:005Lu0:4975Y0:4975)2SiO5 (Nd:LYSO) crystal, an efficient dual-wavelength operation at 1,075 and 1,079 nm is obtained. The maximum output power is 702 mW when the incident pump power is 2.53 W, corresponding to an optical conversion efficiency of 27.7% and a slope efficiency of 37.0%.
The microstructure characteristics of laser forming repaired (LFR) Ti60 (Ti-5.6Al-4.8Sn-2Zr-1Mo-0.35Si-0.3Nb) as-deposited and annealed samples are analyzed. The microstructure of as-deposited repaired zone (RZ) consists of epitaxial columnar prior \beta grains, in which fine woven \alpha laths and \beta-phase between \alpha laths exist. The heat-affected zone (HAZ) experiences a continuous microstructural transition from duplex microstructure of the base metal zone (BMZ) to the microstructure of RZ. The presence of silicide precipitates is observed in both RZ and BMZ in an annealed sample by transmission electron microscopy. They are identified as (Ti, Zr)6Si3 distributed mainly at the \alpha/\beta interface with the size of 100-300 nm. The fine \alpha2 precipitates are detected in BMZ by electron diffraction; there was no \alpha2 detected in RZ.
A high-powered millijoule pulse energy Tm3+-doped fiber amplifier seeded with a Q-switched operation of Tm (4 at.-%), Ho (0.4 at.-%):YVO4 laser is reported. The output characteristics of the amplified laser are studied at the coupled powers of 0.266, 1.24, and 2.65 W. Maximum output power up to 15.7 W is at 10-kHz repetition rate. Nonlinear effects are not observed from the emitting spectrum and the full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the pulse duration is reduced from 40.1 to 25.9 ns at 1.57-mJ pulse energy. The beam quality factor M2x=1.9\pm 0.03, M2y=2.1\pm 0.02 at the output power of 14.5 W is measured using the traveling knife-edge method.
We demonstrate a multi-wavelength erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) using erbium gain and four-wave mixing (FWM) effect in a piece of erbium-doped fiber (EDF) with high erbium ion concentration. The EDF has a pump absorption rate of 24.6 dB/m at 979 nm and is bi-directionally pumped by 980-nm laser diodes. FWM effect redistributes the energy of different oscillating lines and causes multi-wavelength operation. The laser generates more than 22 lines of optical comb with a line spacing of approximately 0.10 nm at the 1569-nm region using only 1.5-m-long EDF.
We address the effects of processing parameters on residual stresses and fatigue properties of LY2 Al alloy by laser shock processing (LSP). Results show that compressive residual stresses are generated near the surface of samples due to LSP. The maximum compressive residual stress at the surface by two LSP impacts on one side is higher than that by one LSP impact. The maximum value of tensile residual stress is found at the mid-plane of samples subjected to two-sided LSP. Compared with fatigue lives of samples treated by single-sided LSP, lives of those treated by two-sided LSP are lower. However, these are higher than untreated ones.
The lifetime of optical components in high-fluence ultraviolet (UV) laser applications is typically limited by laser-initiated damage and its subsequent growth. Using 10.6-μm CO2 laser pulses, we successfully mitigate 355-nm laser induced damage sites on fused silica surface with dimensions less than 200 \mu m. The damage threshold increases and the damage growth mitigates. However, the growth coefficients of new damage on the CO2 laser processed area are higher than those of the original sample. The damage grows with crack propagation for residual stress after CO2 laser irradiation. Furthermore, post-heating is beneficial to the release of residual stress and slows down the damage growth.
Surface-emitting distributed feedback quantum-cascade lasers operating at \lambda \approx 7.8 \mu m are demonstrated. The metal-covered second-order grating is shallow-etched into the surface of a thin InGaAs contact and cladding layer. This forms a hybrid waveguide and used to achieve relatively low waveguide losses and high coupling strengths. The devices exhibit stable single-mode operation from 90 to 130 K with a side mode suppression ratio above 20 dB. A slope efficiency of 194 mW/A is obtained at 90 K, which is twice higher than that of the Fabry-Perot counterpart.
We present a 3~5 \mum optical parametric oscillator (OPO) based on ZGP pumped by KTP OPO 2.1-\mum laser. The tuning curves of ZGP OPO are calculated. The 8 \times 6 \times 18 (mm) ZGP crystal, whose end faces are antireflection coated at 2.1 and 3.7~4.6 \mum, is cut as \theta =53.5o, \phi =0o. When the pump power of 2.1-\mu m polarized laser is 15 W at 8 kHz, 5.7-W output power and 46.6% slope efficiency are obtained with a ZGPtype I phase match. Central wavelengths of the signal and idler lasers are 4.10 and 4.32 μm, respectively. Pulse duration is about 27 ns. Beam quality factor M2 is better than 1.8. The tunability of 3~5 \mu m can be achieved by changing the angle of the ZGP crystal.
The dynamic behavior of an optical micro ring resonator (OMRR) with an amplitude modulator positioned in the micro ring is investigated quantitatively by adopting a recently introduced quantifier, the permutation entropy (PE). The effects of modulation depth are focused on, and the roles of input power are considered. The two-dimensional (2D) maps of PE showing dependence on both modulation depth and input power are presented as well. PE values nearly increase with modulation depth. On the other hand, the optimal value of input power is achieved when the PE reaches its maximum. Thus, PE can successfully quantify the dynamics of modulated OMRR. Selecting the parameters in the region with high PE values would contribute to the complexity-enhanced OMRR-based chaotic communication systems.
Using an external cavity with holographic grating, we demonstrate the spectral narrowing of a high power broad-area-diode with a single emitter. The spectral bandwidth of less than 15 GHz is obtained with output power exceeding 10 W and external cavity efficiency exceeding 60%. Absorption of 98% of the laser radiation by a 25-mm rubidium vapor cell filled with 600-torr ethane at a temperature of 368 K is acquired, which demonstrates the availability of this pump source for efficient rubidium laser pumping.
Morphology evolution of prior \beta grains of laser solid forming (LSF) Ti-xAl-yV (x \leq 11,y \leq 20) alloys from blended elemental powders is investigated. The formation mechanism of grain morphology is revealed by incorporating columnar to equiaxed transition (CET) mechanism during solidification. The morphology of prior \beta grains of LSF Ti-6Al-yV changes from columnar to equiaxed grains with increasing element V content from 4 to 20 wt.-%. This agrees well with CET theoretical prediction. Likewise, the grain morphology of LSF Ti-xAl-2V from blended elemental powders changes from large columnar to small equiaxed with increasing Al content from 2 to 11 wt.-%. The macro-morphologies of LSF Ti-8Al-2V and Ti-11Al-2V from blended elemental powders do not agree with CET predictions. This is caused by the increased disturbance effects of mixing enthalpy with increasing Al content, generated in the alloying process of Ti, Al, and V in the molten pool.
The application of a thermal source in non-contact forming of sheet metal has long been used. However, the replacement of this thermal source with a laser beam promises much greater controllability of the process. This yields a process with strong potential for application in aerospace, shipbuilding, automobile, and manufacturing industries, as well as the rapid manufacturing of prototypes and adjustment of misaligned components. Forming is made possible through laser-induced non-uniform thermal stresses. In this letter, we use the geometrical transition from rectangular to circle-shaped specimen and ring-shaped specimen to observe the effect of geometry on deformation in laser forming. We conduct a series of experiments on a wide range of specimen geometries. The reasons for this behavior are also analyzed. Experimental results are compared with simulated values using the software ABAQUS. The utilization of line energy is found to be higher in the case of laser forming along linear irradiation than along curved ones. We also analyze the effect of strain hindrance. The findings of the study may be useful for the inverse problem, which involves acquiring the process parameters for a known target shape of a wide range of complex shape geometries.
A tunable slow light of 2.5-Gb/s pseudo-random binary sequence signal using a 1550-nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) is experimentally demonstrated. The influences of the bias current and the gain saturation on the slow light are investigated. With bias current increasing, tunable optical group delay up to 98 ps is obtained at room temperature. Demonstration of the time delay between 16 and 24 ps by signal intensity change is reported. Under an appropriate bias current, by tuning the input signal to track the peak gain wavelength of the VCSEL, slow light of a power penalty as low as 1 dB is achieved. With such a low power penalty, the VCSEL has a great potential application as a compact optical buffer.
The development of phased-array grating compressor is a crucial issue for high-energy, ultra-short pulse petawatt-class lasers. Almost all systems have adopted a tiled-grating approach to meet the size requirements for the compression gratings. We present a computer-control test system utilizing near-field interference and far-field focusing capable of monitoring and fast correcting tiled errors of the grating compressor. In this system, the tilt/tip errors between the two gratings are determined by the Fourier transform (FT) of the individual interference fringe, and the piston errors are determined by the ratio of the two primary peaks formed in the far-field pattern as a function of the piston difference. Monochromatic grating phasing is achieved experimentally and pulse compression is demonstrated with a tiled grating system.
A high repetition rate Tm:Ho:LuLiF master-oscillator and polarization-maintaining (PM) Tm-doped fiber power-amplifier system is presented. A 11.3-kHz, 0.4-nm line width, 0.89-W Tm:Ho:LuLiF seed laser is developed. Using a two-stage PM Tm-doped fiber power amplifier system, 32.4-W output power is obtained with 0.4-nm line width at a central wavelength of 2058.5 nm, corresponding to 0.66-W seed laser. The laser spectrum and pulse profile are measured.
A frequency-stabilized 556-nm laser is an essential tool for experimental studies associated with 1S0-3P1 intercombination transition of ytterbium (Yb) atoms. A 556-nm laser light using a single-pass second harmonic generation (SHG) is obtained in a periodically poled MgO:LiNbO3 (PPLN) crystal pumped by a fiber laser at 1111.6 nm. A robust frequency stabilization method which facilitates the control of laser frequency with an accuracy better than the natural linewidth (187 kHz) of the intercombination line is developed. The short-term frequency jitter is reduced to less than 100 kHz by locking the laser to a home-made reference cavity. A slow frequency drift is sensed by the 556-nm fluorescence signal of an Yb atomic beam excited by one probe beam and is reduced to less than 50-kHz by a computer-controlled servo system. The laser can be stably locked for more than 5 h. This frequency stabilization method can be extended to other alkaline-earth-like atoms with similar weak intercombination lines.
A passively mode-locked grown-together composite YVO4/Nd:YVO4 crystal laser is demonstrated with a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror by 880-nm laser-diode direct pumping. Under the absorbed pump power of 24.9 W, a maximum output power of 10.5 W at the repetition rate of 77 MHz is obtained, corresponding to the optical-optical conversion efficiency of 42.1% and the slope efficiency of 53.4%. The pulse width measured is 33 ps at the output power of 10 W.
We measure the phase fluctuation in a high-power fiber amplifier using a multi-dithering technique. Its fluctuation property is qualitatively analyzed by the power spectral density and integrated spectral density. Low frequency fluctuations caused by the environment are dominant in the phase fluctuations in an amplifier, whereas the high frequency components related to laser power affect the control bandwidth. The bandwidth requirement of the active phase-locking is calculated to be 300 Hz, 670 Hz, 1.6 kHz, and 3.9 kHz under the output power of 25, 55, 125, and 180 W, respectively. The approximately linear relationship between the control bandwidth and laser power needs to be further investigated.
We experimentally demonstrate the simultaneous generation of tunable multi-wavelength picosecond laser pulses using a self-seeding configuration that consists of a gain-switched Fabry-Perot laser diode (FPLD) with an external cavity formed by a tilted multimode fiber Bragg grating. Dual- and triple-wavelength pulses are obtained and tuned in a flexible manner by changing the temperature of the FPLD. The side mode suppression ratio larger than 25 dB is achieved at different dual- and triple-wavelengths and the typical pulsewidth of the output pulses is ?70 ps. In the experiment, the wavelength separation can be narrowed to 0.57 nm.
We present a 657-nm external cavity diode laser (ECDL) system, where the output frequency is stabilized by a narrow-band high transmission interference filter. This novel diode laser system emits laser with an instantaneous linewidth of 7 kHz and a broadened linewidth of 432 kHz.
The efficient generation of a 1.17-mJ laser pulse with 360 ps duration using an ytterbium (Yb)-doped fiber amplifier chain seeded by a homemade mode-locked fiber laser is demonstrated experimentally. A specially designed figure-of-eight fiber laser acts as the seed source of a chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) system and generates mode-locked pulses with hundreds of picosecond widths. Two kinds of large-mode-area (LMA) double-clad Yb-doped fibers are employed to construct the pre-amplifier and main amplifier. All of the adopted instruments help avoid severe nonlinearity in fibers to raise sub-nanosecond pulse energy with acceptable signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The output spectrum of this fiber-based CPA system shows that amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) is suppressed to better than 30 dB, and the onset of stimulated Raman scattering is excluded.
We experimentally demonstrate a fast random bit generator (RBG) based on bandwidth-enhanced chaotic laser from an optical feedback laser diode with optical injection. The bandwidth-enhanced chaotic signal is sampled and converted to a binary sequence in real time without the need of programming for off-line processing. Multi-rate bit sequences, with the fastest rate of up to 2.87 Gb/s, are obtained with verified randomness.
An optimized dual fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is proposed for 980-nm semiconductor lasers without thermoelectric coolers to restrict temperature-induced wavelength shift. The mathematical model of the temperature-induced wavelength shift of the laser with the dual FBG is built using the external cavity feedback rate equations. The external cavity parameters are optimized for achieving the stability mode-locking laser output. The spectral characteristics of the dual FBG stabilized laser are measured to range from 0 to 70 oC. The side mode suppression ratio (SMSR) is more than 45 dB, while the full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) is less than 1 nm. The peak wavelength shift is less than 0.1 nm. The dual FBG wavelength shift proportional coefficient is between 0.1086 and 0.4342.
We report an all-fiber high power, single frequency large-mode area (LMA) linearly polarized ytterbiumdoped fiber amplifiers (YDFA) module, which is based on the master oscillator multi-stage power amplifiers (MOPA). The maximum output power is 43.8 W at a wavelength of 1064 nm when 60-W launched pump light is coupled, with high slope efficiency of 88%, polarization extinction rate (PER) >17.2 dB and nearly diffraction-limited beam quality (M2<1.1).
We demonstrate a multiple wavelength Brillouin/erbium fiber laser in a linear cavity configuration. The laser cavity is made up of a fiber loop mirror on one end of the resonator and a virtual mirror generated from the distributed stimulated Brillouin scattering effect on the other end. Due to the weak reflectivity provided by the virtual mirror, self-lasing cavity modes are completely suppressed from the laser cavity. At Brillouin pump and 1480-nm pump powers of 2 and 130 mW, respectively, 11 channels of the demonstrated laser with an average total power of 7.13 dBm can freely be tuned over a span of 37-nm wavelength from 1530 to 1567 nm.
A novel tunable multi-wavelength fiber ring laser based on semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) is proposed by using a high-birefringence (Hi-Bi) fiber loop mirror (FLM) as wavelength filter. With this configuration, the wavelength spacing of this laser can be varied by using the different lengths of Hi-Bi fiber. 8 wavelengths spacing on 450 GHz are experimentally obtained with more than 25-dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for each channel using 1.28-m Hi-Bi fiber in Hi-Bi FLM. The output power variation between different channels is measured to be less than 5.9 dB. The linewidth of each channel is compressed from 0.347 to 0.186 nm by 1.5-m unpumped erbium-doped fiber (EDF). Meanwhile, 17 wavelengths spacing on ITU-gird (100 GHz) are also obtained with 5.9-m Hi-Bi fiber in Hi-Bi FLM. All these channels can be tuned together over 0.4 nm.
Operating a laser diode in an external cavity, which provides frequency-selective feedback, is a very effective method to tune the laser frequency to a range far from its free running frequency. For the Ca atomic Ramsey spectroscopy experiment, we have constructed a 657-nm laser system based on the Littman-Metcalf configuration with a 660-nm commercial laser diode. Continuously 10-GHz tuning range was achieved with about 100-kHz spectral linewidth, measured with beat-note spectrum of two identical laser systems.